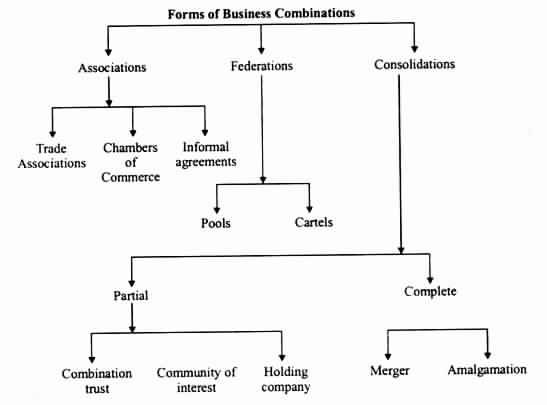
Business Combination Meaning Causes, Objectives
Business combinations are combinations formed by two or more business units, with a view to achieving certain common objective (specially elimination of competition); such combinations ranging from loosest combination through associations to fastest combinations through complete consolidations.
L.H. Haney defines a combination as follows:
“To combine is simply to become one of the parts of a whole; and a combination is merely a union of persons, to make a whole or group for the prosecution of some common purposes.”
Causes of Business Combinations:
(i) Wasteful Competition:
Competition, which is said to be the ‘salt of trade’, by going too far, becomes a very powerful instrument for the inception and growth of business combinations. In fact, competition, according to Haney, is the major driving force, leading to the emergence of combinations, in industry.
(ii) Economies of Large-Scale Organization:
Organisation of production on a large scale brings a large number of well-known advantages in its wake like technical economies, managerial economies, financial economies, marketing economies and economies vis-a-vis greater resistance to risks and fluctuations in economic activities. Economies of large scale operations, thus become, a powerful force causing increased race for combinations.
(iii) Desire for Monopoly Power:
Monopoly, a natural outcome of combination, leads to the control of market and generally means larger profits for business concerns. The desire to secure monopolistic position certainly prompts producers to join together less than one banner.
(iv) Business Cycles:
Trade cycles, the alternate periods of boom and depression, lead to business combinations. Boom period i.e. prosperity period leading to an unusual growth of firms to reap rich harvest of profits results in intense competition; and becomes a ground for forming combinations.
Depression, the times of economic crisis-with many firms having to only option to close down-prompts business units to combine to ensure their survival.
(v) Joint Stock Companies:
The corporate form of business organization is a facilitating force leading to emergence of business combinations. In joint stock companies, control and management of various corporate enterprises can be concentrated, in a ‘small group of powerful persons through acquiring a controlling amount of shares of different companies.
(vi) Influence of Tariffs:
Tariffs have been referred to as “the mother of all trusts”. (A trust is a form of business combinations). Tariffs do not directly result in combinations; they prepare the necessary ground for it. In fact, imposition of tariffs restricts foreign competition; but increases competition among domestic producers. Home producers resort to combinations, to protect their survival.
(vii) Cult of the Colossal (or Respect for Bigness):
In the present-day-world, business units of bigger size are more respected than units of small size. Those who believe in the philosophy of power and ambition, compel small units to combine; and are instrumental in forming powerful business combinations, in a craze for achieving bigness.
(viii) Individual Organising Ability:
The scarcity of organizing talent has also induced the formation of combinations, in the business world. Many-a-times, therefore, combinations are formed due to the ambition of individuals who are gifted with organising ability. The number of business units is far larger than the skilled business magnates; and many units have to combine to take advantage of the organising ability of these business brains.
Objectives
Eliminates Competition
Business combination helps in eliminating the tough competition among firms in market. In presence of a competition, many businesses are not able to earn suitable profits. They come together and set up their combination to work together for achieving common goals.
Proper Management
It leads to proper management of all business units that merged together into one unit. Small business cannot afford the services of quality managers which affects their performance. Combination of these units together enables them in hiring management experts.
Attains Monopoly
Acquiring market dominance is another major objective of business combination. Several businesses by forming a combination attain a monopoly position and enjoy a larger share in market.
Economy Scale
Business combination assist in availing the benefits of economies of scale. Small business units by merging together purchases large amount of raw materials at cheap rate and carrying out their production activities at a large scale. This brings down their cost of operations and increases their profit level.
Solves Capital Problem
It helps in overcoming the capital problems. Small business units lack funds for growing their activities. By associating with other units they easily gets funds for large scale production, buying advanced machinery and carrying out research activities.
Economic Stability
Combination of business impart them greater health to face crisis. By joining as one unit they can easily overcome times of political and economic instability.
Improve Product Quality
It leads to enhance the quality of products and level of production by firms. Combination enables them in sharing ideas, knowledge and technology with each other which results in better production. By combining the efforts they come up with new and advanced products in market.