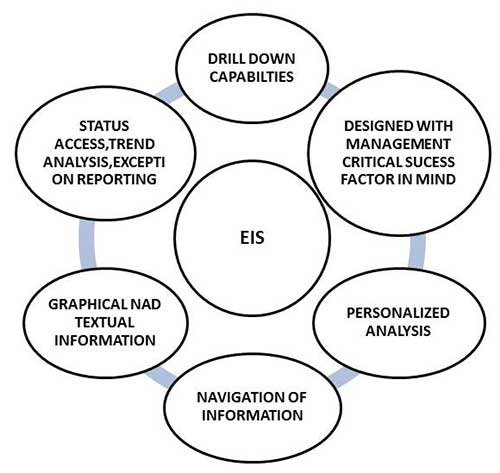
Executive Information Systems, Process, Disadvantages, Role in Decision making process
An Executive Information System can be defined as a specialized Decision Support System. This type of the system generally includes the various hardware, software, data, procedures and the people. With the help of all this, the top level executives get a great support in taking and performing the various types of the decisions. The executive information system plays a very important role in obtaining the data from the different sources, then help in the integration and the aggregation of this data. After performing these steps the resulting information is displayed in such a pattern that is very easy to understand.
Executive information system is ‘a computer based system that serves the information that is needed by the various top executives. It provides very rapid access to the timely information and also offers the direct access to the different management reports.’
Executive Information System is very user friendly in the nature. It is supported at a large extent by the graphics.
Executive support system can be defined as the comprehensive executive support system that goes beyond the Executive Information System and also includes communications, office automation, analysis support etc.
According to Watson, Executive Information System / executive support system depends on some of the factors that can be summarized as the follows
- Internal factors
- Need for the timely information.
- Need for the improved communications.
- Need for the access to the operational data.
- Need for the rapid status updates on the various business activities.
- Need for the access to the corporate database.
- Need for very accurate information.
- Need for the ability to identify the various historical trends.
- External Factors
- Increasing and intensifying the global competition.
- Rapidly changing the business environment.
- Need to be more proactive.
- Need to access the external database.
- Increasing the various government regulations.
Characteristics of the Executive Information System
- Informational characteristics
- Flexibility and ease of use
- Provides the timely information with the short response time and also with the quick retrieval
- Produces the correct information
- Produces the relevant information
- Produces the validated information
- User interface/orientation characteristics
- Consists of the sophisticated self help
- Contains the user friendly interfaces consisting of the graphic user
- Can be used from many places
- Offers secure reliable, confidential access along with the access procedure
- Is very much customized
- Suites the management style of the individual executives
- Managerial / executive characteristics
- Supports the over all vision, mission and the strategy
- Provides the support for the strategic management
- Sometimes helps to deal with the situations that have a high degree of risk
- Is linked to the value added business processes
- Supports the need/ access for/ to the external data/ databases
- Is very much result oriented in the nature
Capabilities of Executive Information System
(i) Helps in accessing the aggregated or macro or global information.
(ii) Provides the user with an option to use the external data extensively.
(iii) Enables analysis of the address and the hoc queries.
(iv) Shows the trends, the ratios and the various deviations.
(v) Helps in incorporating the graphic and the text in the same display, which helps to have a better view.
(vi) It helps in the assessment of the historical as also the latest data.
(vii) Problem indicators can be highlighted with the help of the Executive Information System / executive support system.
(viii) Open ended problem explanation with the written interpretations can be done with the help of the Executive Information System / executive support system.
(ix) Offers management by the exception reports.
(x) Utilizes the hyper text and the hyper media.
(xi) Offers generalized computing.
(xii) Offers telecommunications capacity.
Executive Information System Process
-
Data Collection:
EIS gathers data from various internal and external sources, including databases, reports, and external data feeds.
-
Data Processing:
The collected data undergoes processing, including validation, aggregation, and transformation to ensure accuracy and relevance.
-
Data Storage:
Processed data is stored in a centralized repository, often a data warehouse, for easy retrieval and analysis.
-
Information Retrieval:
Executives can query the EIS to retrieve specific information based on their needs. The system uses user-friendly interfaces for ease of interaction.
-
Data Analysis and Reporting:
EIS provides tools for data analysis, generating reports, summaries, and visualizations that offer insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and relevant metrics.
-
Trend Identification:
The system identifies trends and patterns within the data, allowing executives to understand historical performance and anticipate future developments.
-
Decision Support:
EIS assists executives in decision-making by providing relevant and timely information. It may include decision support tools and models for scenario analysis.
-
Alerts and Notifications:
EIS monitors predefined thresholds and conditions, triggering alerts or notifications to executives when significant events or deviations occur.
-
Strategic Planning Support:
EIS contributes to strategic planning by offering insights into market trends, competitive intelligence, and the organization’s overall performance.
-
Integration with External Data:
EIS often integrates with external data sources, such as industry reports, economic indicators, and market research, to provide a comprehensive view.
-
Customization for Executives:
EIS is customizable to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual executives, allowing them to focus on the information most relevant to their roles.
-
User Interface and Accessibility:
EIS features user-friendly interfaces that provide easy access to information, ensuring that executives can quickly navigate and retrieve the data they require.
-
Feedback Mechanism:
Executives can provide feedback on the usefulness and relevance of the information provided, contributing to system refinement and improvement.
-
Security Measures:
EIS incorporates robust security measures to safeguard sensitive executive-level information and ensure data confidentiality.
Benefits of Executive Information System
(i) Achievement of the various organizational objectives.
(ii) Facilitates access to the information by integrating many sources of the data.
(iii) Facilitates broad, aggregated perspective and the context.
(iv) Offers broad highly aggregated information.
(v) User’s productivity is also improved to a large extent.
(vi) Communication capability and the quality are increased.
(vii) Provides with the better strategic planning and the control.
(viii) Facilitates pro-active rather than a reactive response.
(ix) Provides the competitive advantage.
(x) Encourages the development of a more open and active information culture.
(xi) The cause of a particular problem can be founded.
Executive Information System Disadvantages
-
Costly Implementation:
The initial investment in designing, implementing, and maintaining an EIS can be substantial, including costs for hardware, software, training, and ongoing support.
-
Complexity and Customization:
EIS can be complex to implement, and customization to fit specific executive needs may require a high level of expertise and effort.
-
Dependency on Data Quality:
The effectiveness of EIS is highly dependent on the quality of the underlying data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed insights and decisions.
-
Integration Challenges:
Integrating EIS with existing information systems within the organization can be challenging, especially in environments with diverse data sources and formats.
-
Resistance to Change:
Executives and organizational members may resist adapting to new technologies and processes, potentially hindering the successful adoption of EIS.
-
Security Concerns:
EIS often deals with sensitive and confidential information. Ensuring robust security measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches.
-
Learning Curve:
Executives and users may face a learning curve when using new EIS tools and interfaces, which can temporarily impact productivity.
-
Overemphasis on Technology:
Overreliance on EIS may lead to a reduction in the importance of human intuition and experience in decision-making, potentially overlooking nuanced aspects.
-
Limited Flexibility:
Some EIS solutions may lack flexibility to adapt quickly to changes in business environments or evolving executive information needs.
-
Maintenance Requirements:
Ongoing maintenance is essential for EIS to remain effective. This includes updates, troubleshooting, and ensuring compatibility with evolving technologies.
-
Data Overload:
EIS, when presenting a large volume of information, may lead to information overload for executives, making it challenging to focus on critical data points.
-
Potential for Misinterpretation:
Executives may misinterpret presented information, especially if they lack a comprehensive understanding of the data sources, models, or assumptions used.
-
Dependency on IT Support:
Executives may become overly dependent on IT support for system-related issues, potentially slowing down decision-making in case of technical problems.
-
Ethical Considerations:
The use of EIS raises ethical concerns related to the privacy and responsible use of sensitive information, requiring organizations to establish clear guidelines and policies.
Executive Information System Role in Decision making process
-
Access to Critical Information:
EIS provides top executives with quick and easy access to critical information relevant to their roles. This information includes key performance indicators (KPIs), financial metrics, market trends, and strategic data.
-
Real-Time Data Monitoring:
Executives can monitor real-time data through EIS, allowing them to stay informed about the current state of the organization and external factors that may impact decision-making.
-
Strategic Planning Support:
EIS assists in strategic planning by offering insights into long-term trends, market dynamics, and competitive intelligence. Executives can align organizational goals with available resources and external opportunities.
-
Decision Support Tools:
EIS incorporates decision support tools such as data analytics, modeling, and scenario analysis. These tools help executives evaluate various decision options and their potential outcomes.
-
Performance Measurement:
Executives can use EIS to measure the performance of different departments, business units, or projects, enabling data-driven assessments and informed decision-making.
-
Risk Management:
EIS supports risk management by identifying potential risks and uncertainties. Executives can use this information to develop strategies for mitigating risks and making more informed decisions.
-
Facilitation of Communication:
EIS facilitates communication among top executives by providing a centralized platform for sharing information, insights, and collaborative decision-making.
-
Aggregation of Information:
EIS aggregates information from diverse sources, including internal databases, external market reports, and operational systems. This aggregation provides a comprehensive view for decision-makers.
-
Customization for Executives:
EIS allows executives to customize dashboards and reports based on their specific information needs. This ensures that executives focus on the most relevant data for their decision-making processes.
-
Performance Evaluation:
Executives can use EIS to evaluate the performance of strategic initiatives, allowing for adjustments and refinements in alignment with organizational goals.
-
Alerts and Notifications:
EIS includes alert mechanisms that notify executives of critical events or deviations from established benchmarks, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Benchmarking:
Executives can compare the organization’s performance against industry benchmarks and competitors, aiding in strategic positioning and goal setting.
-
Data Visualization:
EIS employs data visualization techniques such as charts and graphs to present complex information in a visually comprehensible format, aiding executives in understanding trends and patterns.
-
Feedback Loop:
EIS establishes a feedback loop where executives can provide feedback on the effectiveness of decisions made and the relevance of information presented, contributing to continuous improvement.