Communication technologies have become advanced since last decade of the twentieth century that accelerated the process of globalization. Presently most of the nations are ready for the electronic economy and to build e-business infrastructure. It is necessary for different countries to develop specialized e-business strategies that exploit their unique capabilities and resources, and even geographic positions. There is also a need for a variety of models for building e-business infrastructure and participating in global e-commerce. Global e-business is growing speedily and several trillion dollars are being exchanged annually over the web. Companies must assess global markets and broaden online in developed countries as well as in the emerging economies of other nations like China, Brazil, and India to exploit the technology of global e-business. Companies may proactively utilize global e-business opportunities and take benefits of e-commerce, or may implement a protective approach to new global competition that intimidates their business. Domestic businesses will progressively feel more pressure of international competition as e-business will offer companies a platform to fight at universal level.
The combination of telecommunications and computer technology has initiated business organizational system known as the internet that offered example of ecological business development. The internet symbolizes a new and important technology that has received more attention from academicians, entrepreneurs, business and investors (Sawhney and Zabin, 2002). The expansion of e-commerce, facilitated through the internet as a channel, suggests both the emergence of a new business environment, and the likelihood of catastrophic change within the previous environment. The emergence of the information age and the initiation of the internet have resulted in transformations and these outcomes forced companies to review their organizational models used to explain business management. Hannan and Freeman (1977) developed the basis of organizational ecology in an attempt to describe the existence of organizations. Since then, organizational ecologists have theorized that environmental pressures considerably impact the triumph of an organization with regard to its form, function, and overall strategy.
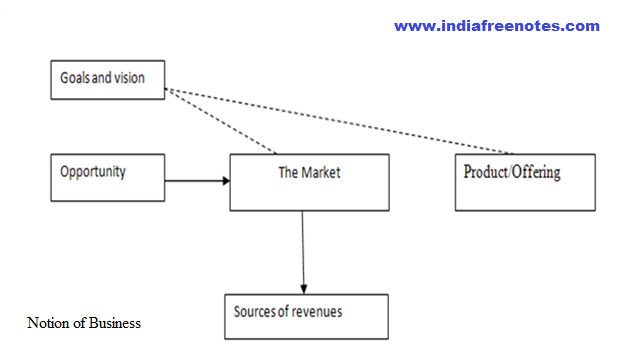
A critical assessment of the growth of e-commerce on the internet gives a distinctive opportunity to scrutinize the natural development of a business sector that was created and colonized over a relatively short time period. Clearly, the internet technology and its different manifestations such as e-commerce provide better opportunities for companies around the world to establish unique strategic advantages (Varadarajan and Yadav, 2002). Global e-commerce is basically about leveraging electronic networks to capture global markets, and it includes all transactions taking place in the worldwide electronic market space. Transactions between global purchaser and sellers can take the form of business-to business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), business to-government (B2G), and other hybrid forms of transactions.
Global E-Enabled Business Process Transformations and Challenges
Integration of digital technology into the business processes has considerably transformed the traditional ways of doing business.
Some of the changes brought about by e-business are summarized below:
(i) Physical marketplace to virtual market-space
The Internet has transformed the traditional ways of buying and selling of goods at physical marketplaces into virtual market-space enabling almost unlimited movements beyond physical borders.
(ii) Physical products to digital products
Breakthroughs in ICT have made possible to sell and buy some products online. For instance, computer software, music, movies, video games, drawings, designs, research papers, reports, and even books can be accessed, evaluated, bought, and downloaded over the net.
(iii) Mass production of standardized products to mass customization
Consequent to industrial revolution in the eighteenth century, the large-scale production of standardized products was used as the most significant tool to achieve scale economies and competitiveness.
Advent of electronic technology and Internet facilitated real-time interaction and information-sharing between the businesses and their various stakeholders, especially the customers and suppliers that made it possible to integrate manufacturing systems to produce customized products for different customers.
(iv) Fixed pricing to dynamic pricing
E-business models offer flexibility in price determination in several ways, such as buyer-determined customized pricing, dynamic pricing by way of online auctions, unlike the traditional fixed-pricing approach.
(v) Mass marketing techniques to customized marketing
Traditional marketing heavily relied upon mass marketing techniques with some adaptations for different market segments. Advent of ICT has facilitated businesses to gather information about individual customers’ tastes and preferences, their buying behaviour and customized marketing strategy to cater to each of the customers.
(vi) Hierarchical organizations to network organizations
The traditional ‘hierarchical organizational structures’ are transforming into ‘network organizational structures’ so as to take benefit of emerging e-business opportunities and meet the potential challenges.
However, businesses going online face several challenges, including:
- As most businesses are making their online presence, the market competition has grown multi-fold from local to global level.
- Online buying and selling of goods often results in elimination of market intermediaries; the process is frequently referred to as ‘disintermediation’, and leads to channel conflict.
- Increase in availability of information online on the public domain augments the chances of its copying by the competitors who make its use for their own benefits.
- Since the Internet can be accessed from across the world, there is no single binding legal framework.
- Most businesses and customers often fear breach of security in terms of both the theft and misuse of classified and personal information over the Internet.
- A large segment of customers is resistant to carrying out business transactions over the Internet.
- Viability of carrying out business transactions differs across firms, depending upon their nature of business and resource availability.
Global E-Business Applications
Integration of ICT finds wide applications in a range of business activities, including the following:
-
E-auctions
In traditional auctions, buyers and sellers gather at an agreed place, often the auction house, at a pre-determined time. Bids are usually placed over and above the reserved price set by the seller until the biding stops at a higher offer rate and the final bidder makes claims to the goods. Using a similar approach, electronic auction sites allow Internet users either to sell or bid for the products offered.
Auction sites generally serve as a forum of buying and selling and charge a commission on sales made. Sellers may post an item they wish to sell along with a minimum price and the deadline to close the auction. Moreover, some site also allows addition of conditions of sales and product photographs.
On the other hand, bidders may explore the site to check its availability and place a bid, usually in designated increments. EBay allows people to buy and sell almost anything.
In some sites, such as liquid price(dot)com, the ‘reverse-auction’ model is used which allows buyers to set the price that sellers compete to match or even beat. A reverse price is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
-
E-banking
The banking industry is a pioneer in using EDI for intra-bank transfer of funds using the SWIFT network. E-banking allows its customers to access their accounts using the Internet and make online transactions with no extra charge.
Besides, banks compete with each other to offer a variety of value-added services to their customers, such as checking their balances, account statements, fund transfers, bill payment, transactions in the stock and commodity markets, customer service, etc.
As a result, customers have access to banking services 24 hours a day and seven days in a week. E-banking has transformed the business processes and its relationship with customers in the banking industry.
-
E-directories
Telephone directories, the so-called ‘white pages’ containing private telephone numbers and the ‘yellow pages’ for businesses have widely been used to locate a person or a company. Conversion of traditional directories from paper to electronic form and integrating them with the Internet has facilitated their online access round the clock from any part of the world.
Besides, a large number of online directories allow users to update their entries any time they wish, irrespective of their geographical locations. Thus the information which could earlier be updated only at the time of printing a new or revised directory has become dynamic in nature.
Moreover, electronic directories are often user-friendly. Users may online access detailed information upon entering the desired fields. For instance, one can get the name and complete address of a person or a company by entering only the telephone number.
-
E-manufacturing
Integration of technology has facilitated sharing real-time information with a firm’s customers and trading partners, leading to the use of such information for making collaborative production decisions.
As a result, businesses are increasingly adopting e-manufacturing using real-time information on customer needs and preferences and productive capacity across the entire supply-chain so as to speedily deliver customized products directly to the customers rather than huge volumes of mass production to fulfil anticipated demands.
An automated manufacturing system integrated through computer technology is known as computer integrated manufacturing (CIM). With globalization of markets and production and with the advent of the Internet, CIM has evolved into a web- centric collaborative venture, termed as e-manufacturing.
E-manufacturing involves Computer-Added Designs (CAD), robots, automated guided vehicles. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), and Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS).
-
E-business Research
The uses of electronic surveys for business research have increased tremendously in the last decade. Due to variation in the extent of availability of personal computers and Internet penetration, mass electronic surveys are possible only in a few developed countries while stratified sampling for select market segments can even be carried out in developing countries.
With the intensification of cyber cafes in India and other emerging economies, the Internet has the reach of far greater population than that captured in most multilateral surveys and publications. Hence, business and institutional surveys are gaining popularity even in the developing countries.
Although electronic surveys are cost-effective and quick, the sample surveyed may not be representative of the population and may lead to faulty inferences. Therefore, due care is to be taken while selecting samples for electronic surveys.
-
E-governance
Governments across the world are using the Internet to augment their communication systems with their citizens. Government websites often provide a wealth of information which is extensively used by various stakeholders, such as foreign and multilateral agencies, officials, researchers, and most importantly by their own citizens.
In addition to information provided, governments across the world are evolving new systems to integrate technology for providing value-added services.
Integration of technology with a system of governance has made it possible to make online queries, file complaints, make applications for various statutory approvals, receive approvals online, and track online interactions. E-governance has significantly contributed to transparency and efficiency in public administration.