Regulations are very important for the growth of capital markets all through the world. The development of a market economy is dependent on the growth of the capital market. The regulation of a capital market encompasses the regulation of securities. These rules enable the capital market to function more competently and fairly.
A well regulated market has the prospective to boost additional investors to participate, and contribute in, promoting the development of the economy.
Capital Market Regulatory Authorities Worldwide: The chief capital market regulatory authorities worldwide are as follows:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
- Canadian Securities Administrators, Canada
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission
- Securities and Exchange Commission, Pakistan
- Securities and Exchange Commission, Bangladesh
- Securities and Exchange Surveillance Commission
- Securities and Futures Commission, Hong Kong
- Financial Supervision Authority, Finland
- Financial Supervision Commission, Bulgaria
- Financial Services Authority, UK
- Commission Nacional del Mercado de Valores, Spain
- Authority of Financial Markets
It has been well established that there is a growing network of financial intermediaries that operate in a highly competitive environment while being directed by strict norms. India has one of the most refined new equity issuance markets. Disclosure requirements and the accounting policies followed by listed companies to offer financial information are comparable to the best systems in the world. In Indian scenario, the securities market is regulated by various agencies such as department of economic affairs, department of company affairs, and the reserve bank of India. The capital markets and protection of investor’s interest is now primarily the responsibility of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which is located in Bombay. The activities of these agencies are coordinated by high level committee on capital and financial market. The high level coordinated committee for financial market discusses various policy level issues which require inter regularity coordination between the regulators in financial market such as RBI, SEBI, insurance, regulatory and development authority (IRDA) and pension regulatory and development authority. The committee is chaired by Governor, RBI, secretary minister of finance, chairman SEBI, chairman IRDA, and chairman, PRDA are members of committee.
The capital market is market of equity and debt securities is regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has full autonomy and authority to regulate and develop capital market. The government has framed rules under securities controls act, the SEBI act and depositories act.
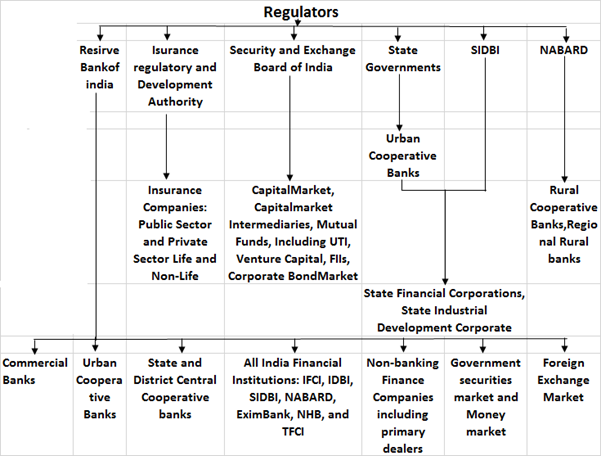
SEBI’s functions include:
- Regulating the business in stock exchange and any other securities markets.
- Registering and regulating the working of collective investment schemes, including mutual funds.
- Barring fraudulent and unfair trade practices relating to securities markets.
- Promoting investor’s education and training of intermediaries of securities markets.
- Prohibiting insider trading in securities, with the imposition of monetary penalties, on erring market intermediaries.
- Regulating substantial acquisition of shares and takeover of companies.
- Calling for information from, carrying out inspection, conducting inquiries and audits of the stock exchanges and intermediaries and self-regulatory organizations in the securities market.
To summarize, Capital market is controlled by financial supervisors and their own governance organization. Major grounds of regulation are to keep investors away from scam and deception. Financial regulatory organizations are also charged with decreasing the losing rate of financial, providing licenses to financial service providers, and executing applicable regulations.
One thought on “Regulatory framework in the Indian Debt Market”