Future Value (FV) is the value of a current asset at a future date based on an assumed rate of growth. The future value (FV) is important to investors and financial planners as they use it to estimate how much an investment made today will be worth in the future. Knowing the future value enables investors to make sound investment decisions based on their anticipated needs.
FV calculation allows investors to predict, with varying degrees of accuracy, the amount of profit that can be generated by different investments. The amount of growth generated by holding a given amount in cash will likely be different than if that same amount were invested in stocks; so, the FV equation is used to compare multiple options.
Determining the FV of an asset can become complicated, depending on the type of asset. Also, the FV calculation is based on the assumption of a stable growth rate. If money is placed in a savings account with a guaranteed interest rate, then the FV is easy to determine accurately. However, investments in the stock market or other securities with a more volatile rate of return can present greater difficulty.
Future Value (FV) formula assumes a constant rate of growth and a single upfront payment left untouched for the duration of the investment. The FV calculation can be done one of two ways depending on the type of interest being earned. If an investment earns simple interest, then the Future Value (FV) formula is:
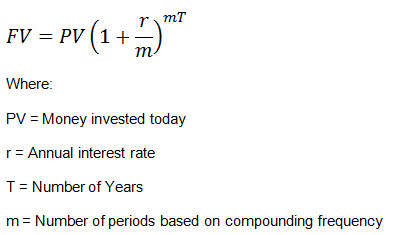
- Future value (FV) is the value of a current asset at some point in the future based on an assumed growth rate.
- Investors are able to reasonably assume an investment’s profit using the future value (FV) calculation.
- Determining the future value (FV) of a market investment can be challenging because of the market’s volatility.
- There are two ways of calculating the future value (FV) of an asset: FV using simple interest and FV using compound interest.
Functions of Future Value:
-
Investment Growth Measurement:
FV is used to calculate how much an investment will grow over time. By applying a specified interest rate, investors can estimate the future worth of their initial investments or savings, helping them understand the potential returns.
-
Retirement Planning:
FV plays a critical role in retirement planning. Individuals can determine how much they need to save today to achieve a desired retirement income. By calculating the future value of regular contributions to retirement accounts, they can set realistic savings goals.
-
Loan Repayment Calculations:
For borrowers, FV is crucial in understanding the total amount owed on loans over time. It helps them visualize the long-term cost of borrowing, including interest payments, aiding in budgeting and financial decision-making.
-
Comparison of Investment Opportunities:
FV provides a standardized way to compare different investment options. By calculating the future value of various investment opportunities, investors can evaluate which options offer the highest potential returns over a specified period.
-
Education Funding:
Parents can use FV to plan for their children’s education expenses. By estimating future tuition costs and calculating how much they need to save now, parents can ensure they accumulate sufficient funds by the time their children enter college.
-
Inflation Adjustment:
FV helps investors account for inflation when planning for future expenses. By incorporating an expected inflation rate into future value calculations, individuals and businesses can better estimate the amount needed to maintain purchasing power over time.
Future Value of a Single Flow:
This occurs when a single sum of money is invested for a certain period at a given interest rate.
Formula:
FV = PV × (1+r)^n
Example:
Suppose ₹10,000 is invested for 3 years at 10% annual interest.
| Year | Calculation | Future Value (₹) |
|---|---|---|
|
3 |
₹10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^3 |
₹13,310 |
So, FV = ₹13,310
Future Value of Uneven Cash Flows:
This involves different amounts of money invested or received at the end of each period. Each flow is treated separately to calculate its FV.
Formula:
 Example:
Example:
You invest the following amounts at 10% interest:
| Year | Cash Flow (₹) |
Years to Compounding |
FV Calculation |
FV (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
2,000 | 3 | 2000 × (1 + 0.10)^3 | 2,662 |
| 2 | 3,000 | 2 | 3000 × (1 + 0.10)^2 | 3,630 |
| 3 | 5,000 | 1 | 5000 × (1 + 0.10)^1 | 5,500 |
| — | Total FV | — | — |
11,792 |
So, Future Value of Uneven Cash Flows = ₹11,792
Future Value of an Annuity:
An annuity is a series of equal cash flows occurring at regular intervals. There are two types: Ordinary Annuity (end of period) and Annuity Due (beginning of period). Here we consider Ordinary Annuity.
Formula:

Example:
You invest ₹2,000 at the end of each year for 3 years at 10% interest.
| Year | Cash Flow (₹) | FV Factor @10% (Years Left) | FV (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2,000 | (1 + 0.10)^2 = 1.21 | 2,420 |
| 2 | 2,000 | (1 + 0.10)^1 = 1.10 | 2,200 |
| 3 | 2,000 | (1 + 0.10)^0 = 1.00 | 2,000 |
| — | Total FV | — | 6,620 |
FV = 2,000 × ((1+0.10)^3−10.10) = 2,000 × 3.31 = ₹6,620
Conclusion
Understanding Future Value is essential for making investment decisions. It helps assess whether current investments will meet future financial goals.
-
Use Single Flow FV for lump-sum investments.
-
Use Uneven Flow FV for irregular cash inflows.
-
Use Annuity FV for regular, equal payments like EMIs, SIPs, or pensions.
One thought on “Future Value, Functions, Types”