Strategy Implementation is the process of turning a chosen strategic plan into actionable steps that achieve organizational goals. It involves aligning the company’s resources, structure, processes, and culture with the strategic objectives. This includes assigning responsibilities, developing budgets, designing organizational systems, and ensuring effective communication and leadership. Successful implementation requires coordination among departments, consistent monitoring, and flexibility to adapt to unforeseen changes. It bridges the gap between strategy formulation and actual performance, ensuring that strategic intentions lead to measurable results. Without proper implementation, even the best-formulated strategies may fail to deliver desired outcomes, making this phase critical to overall business success.
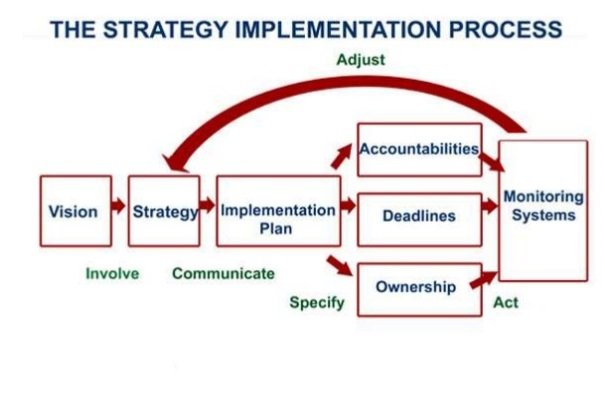
Process of Strategic Implementation:
-
Defining Clear Objectives and Goals
The first step in strategic implementation is to break down the overall strategy into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. These goals provide clarity and direction for every level of the organization. Clearly defined objectives help ensure that everyone understands what needs to be achieved and how their roles contribute to the broader strategic vision. This step aligns individual, departmental, and organizational performance targets with the strategic intent, enabling accountability. Effective goal-setting motivates teams, sets expectations, and provides benchmarks against which progress and success can be measured over time.
-
Aligning Organizational Structure and Resources
Once the objectives are set, the organization’s structure must be adjusted or realigned to support the implementation of the strategy. This includes defining roles, delegating responsibilities, and ensuring clear reporting relationships. Human, financial, technological, and physical resources should be allocated efficiently to the strategic priorities. The right people must be placed in the right positions to carry out tasks effectively. Without proper alignment of structure and resources, strategy execution may suffer from inefficiencies, delays, or miscommunication. This phase also includes creating cross-functional teams or new units where necessary to support the new strategic direction.
-
Developing Supporting Policies and Procedures
Policies and procedures are the rules, guidelines, and routines that govern daily operations. During implementation, organizations must develop or revise their internal policies to ensure consistency with the strategy. This could involve changes to HR practices, procurement methods, quality control standards, or customer service protocols. Policies should support the strategic goals by promoting desired behaviors, decision-making processes, and accountability systems. Clear procedures eliminate confusion, standardize operations, and enable the workforce to act confidently. Without strategic alignment in policies, employees may unknowingly act in ways that conflict with the organization’s long-term goals.
-
Ensuring Effective Communication and Leadership
Strong leadership and clear communication are critical for successful strategy implementation. Top management must communicate the strategic goals, expected outcomes, and individual responsibilities across all levels of the organization. Regular meetings, internal newsletters, training sessions, and workshops are effective channels for communication. Leaders must also listen to employee feedback, address concerns, and motivate teams. Transparency builds trust and encourages commitment to the strategy. Leadership plays a crucial role in resolving conflicts, removing implementation roadblocks, and modeling the behavior necessary for strategic success. An engaged and informed workforce performs more cohesively and efficiently.
-
Monitoring, Evaluation, and Control
The final phase involves continuously monitoring progress against defined objectives and making adjustments as necessary. Organizations must set up key performance indicators (KPIs), dashboards, and review mechanisms to track implementation. Regular audits, feedback sessions, and performance appraisals help identify issues early and guide corrective action. This step ensures that the strategy remains on course and is responsive to changes in the internal or external environment. Continuous evaluation helps maintain momentum, correct deviations, and learn from experiences. It also reinforces a culture of accountability and excellence, increasing the likelihood of long-term strategic success.
Aspects of Strategic Implementation:
-
Organizational Structure Alignment
The structure of the organization must support the strategic plan. This includes clear roles, responsibilities, reporting lines, and coordination mechanisms. A well-aligned structure ensures that tasks flow logically, decision-making is streamlined, and resources are optimally used. For example, implementing a global expansion strategy might require a shift from a functional to a divisional structure.
-
Resource Allocation
Strategic implementation requires careful allocation of financial, human, technological, and physical resources. Resources must be directed toward priority projects and initiatives that support the strategy. Proper budgeting, staffing, and technology support are essential to avoid bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
-
Leadership and Management Support
Effective leadership is crucial in guiding the organization through the change process. Leaders must provide vision, motivation, direction, and resolve conflicts. They play a key role in championing the strategy, aligning teams, and ensuring that strategic goals are understood and embraced at every level.
-
Communication System
Clear and consistent communication is vital. The strategic intent, goals, and expected roles must be communicated throughout the organization. Two-way communication helps in managing resistance, encouraging feedback, and ensuring all employees understand the importance of their contributions to the strategy.
-
Performance Monitoring and Control
Monitoring systems such as KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), dashboards, and performance reviews track progress and highlight deviations. Strategic control involves timely corrective actions, process improvements, and adaptations to changes in the environment or internal capabilities.
-
Culture and Change Management
Organizational culture must support the strategy. If a strategy calls for innovation, but the culture resists change, implementation will fail. Change management processes—including training, engagement initiatives, and leadership modeling—help align culture with strategy.
-
Policies and Procedures
Policies and standard operating procedures (SOPs) must be aligned with strategic priorities. They guide daily decision-making and ensure consistency in action. Without supporting policies, strategic decisions may not be implemented effectively or uniformly across departments.
-
Strategic Fit and Synergy
All parts of the organization (functions, departments, processes) must work together in harmony toward common goals. Strategic fit ensures alignment across functions, while synergy means that the combined performance is greater than the sum of individual efforts.
-
Technology and Information Systems
Technology supports strategy execution by improving efficiency, enabling data-driven decisions, and enhancing communication. Information systems must be in place to provide real-time data, track outcomes, and support performance analysis.
-
Motivation and Incentive Systems
Employee motivation is a critical aspect. Incentive programs—monetary or non-monetary—should be aligned with strategic objectives. Recognition and rewards systems help reinforce desired behaviors and drive performance toward strategic goals.