Strategy Implementation: Aspects of Strategy Implementation
20/03/2020Strategy implementation is the translation of chosen strategy into organizational action so as to achieve strategic goals and objectives. Strategy implementation is also defined as the manner in which an organization should develop, utilize, and amalgamate organizational structure, control systems, and culture to follow strategies that lead to competitive advantage and a better performance. Organizational structure allocates special value developing tasks and roles to the employees and states how these tasks and roles can be correlated so as maximize efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction-the pillars of competitive advantage. But, organizational structure is not sufficient in itself to motivate the employees.
Strategic implementation is critical to a company’s success, addressing the who, where, when, and how of reaching the desired goals and objectives. It focuses on the entire organization. Implementation occurs after environmental scans, SWOT analyses, and identifying strategic issues and goals. Implementation involves assigning individuals to tasks and timelines that will help an organization reach its goals.
An organizational control system is also required. This control system equips managers with motivational incentives for employees as well as feedback on employees and organizational performance. Organizational culture refers to the specialized collection of values, attitudes, norms and beliefs shared by organizational members and groups.
Following are the main steps in implementing a strategy:
- Developing an organization having potential of carrying out strategy successfully.
- Disbursement of abundant resources to strategy-essential activities.
- Creating strategy-encouraging policies.
- Employing best policies and programs for constant improvement.
- Linking reward structure to accomplishment of results.
- Making use of strategic leadership.
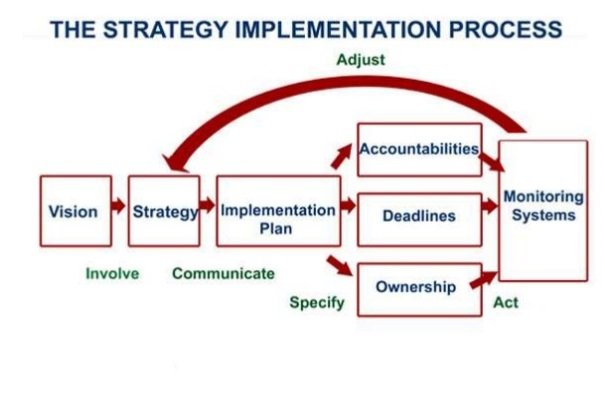
Excellently formulated strategies will fail if they are not properly implemented. Also, it is essential to note that strategy implementation is not possible unless there is stability between strategy and each organizational dimension such as organizational structure, reward structure, resource-allocation process, etc.
Strategy implementation poses a threat to many managers and employees in an organization. New power relationships are predicted and achieved. New groups (formal as well as informal) are formed whose values, attitudes, beliefs and concerns may not be known. With the change in power and status roles, the managers and employees may employ confrontation behaviour.
Aspects of Strategic Management
Strategic management is the process of evaluating the best policies for a business’s managers to carry out in order to achieve the organization’s goals and priorities. As a small-business owner, you can create a competitive advantage for your company by enacting aspects of strategic management.
(i) Strategic Analysis
Strategic analysis is an idea used within the broader field of strategic management to help businesses understand where their companies fit into the broader marketplace. This starts by looking inward evaluating the work environment, the availability of resources and the relationships between various levels of stakeholders. The aim of strategic analysis is to get you, the business owner or manager, to think about the key influences on the company’s present position and to begin thinking about how those influences can be manipulated to get the company where it wants or needs to go.
(ii) Strategic Choice
Once a strategic analysis of the company’s environment has been carried out, you can move onto listing the strategic choices your company can take to meet its objectives. If you need to increase revenue by 25 percent, for instance, over the next 12 months, listing your strategic choices will help you come up with ways to scale up resources, change company policy and reinvent business processes so as to reach the increased revenue goal. The key to this process is open communication. Discussing your options with your stakeholders employees, customers, board members and concerned community members will give you a 360-degree view of where the company can tweak or modify its policies and processes to better position itself for success.
(iii) Strategy Implementation
Implementing the choices outlined in the strategic plan is likely to be a time-consuming and, at times, frustrating endeavor. There are two things to keep in mind allocation of resources and the organizational structure. If the organization and its management are rigid and not very open to change, it will be much harder to implement your strategic plan. You also have to think about access to resources, such as manpower, money and tools. Implementing change within the business will require a balance between pouring money into a problem and effectively using resources to change business policies and processes.
(iv) SWOT Analysis
One of the main tools that can be used in bringing together a strategic management plan is called a SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The idea behind this tool is to list each of your organization’s attributes in each section. If you have strengths in customer service, list that here, but also don’t be shy about listing areas for improvement. If your facilities need to be revamped, list that as an opportunity to better your company. If there’s a competitor you can’t do much to control, list that as a weakness. Seeing all of your business’s pros and cons in one place can you help decide a strategic plan for accomplishing financial, operations and resource-based goals.