-
Successful Money Management
A. Money management: The day-to-day financial activities necessary to manage current personal economic resources while working toward long-term financial security.
B. Opportunity Cost and Money Management
-
-
- Spending money on current living expenses reduces the amount you can use for saving and investing for long-term financial security.
- Saving and investing for the future reduce the amount you can spend now.
- Buying on credit results in payments later and reduces the amount of future income available for spending.
- Using savings for purchases results in lost interest earnings and an inability to use savings for other purposes.
- Comparison shopping can save you money and improve the quality of your purchases but uses up something of value you cannot replace: your time.
-
C. Components of Money Management
-
-
- Personal Financial Records and Documents
- Personal Financial Statements
- A Budget or Spending Plan
-
A System for Personal Financial Records
-
3. Personal Financial Statements
A. The Personal Balance Sheet: Where are You Now?
Items of Value – Amounts Owed = Net Worth
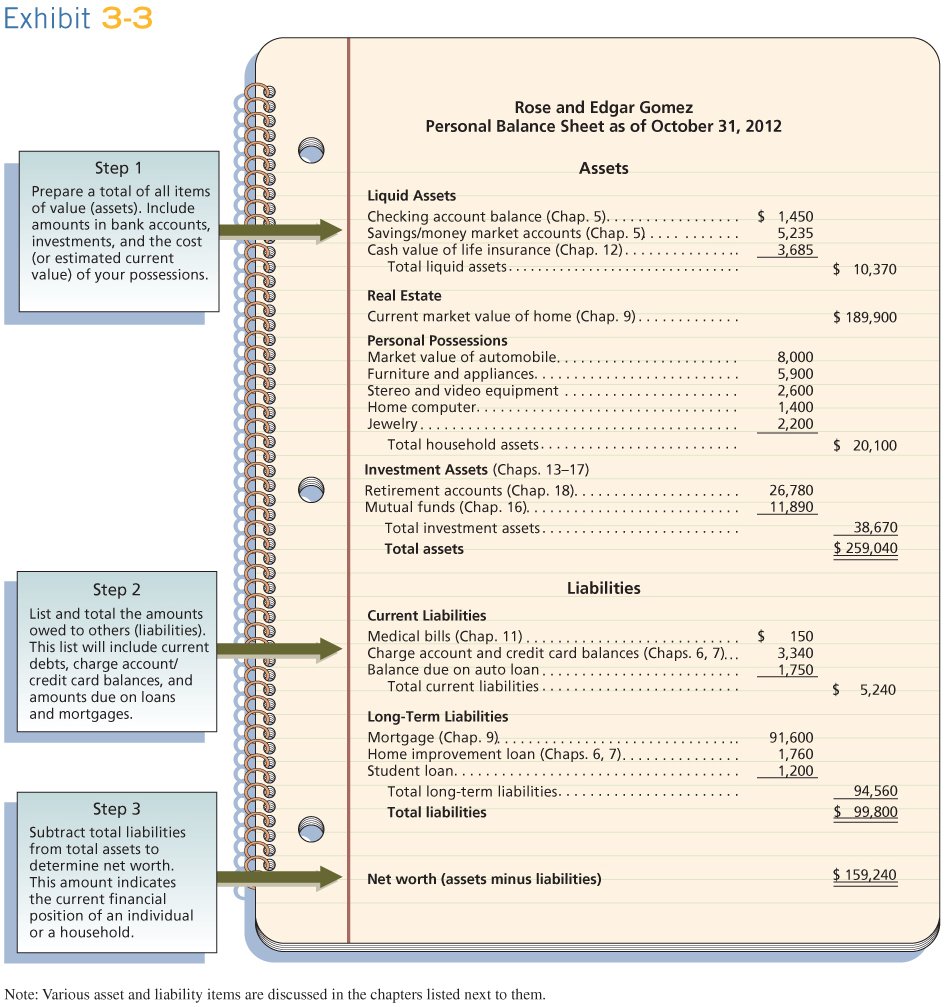
B. Evaluating Your Financial Positiion
If you are a traditional college student, don’t be surprised if your net worth is negative.
C. The Cash Flow Statement: Where Did Your Money Go?
Total Cash Received during the time period – Cash Outflow during the time period = Cash Surplus or Deficit