Scope:
This standard shall be applied in the accounting for and disclosure of events after the reporting period. There would always be a gap between the end of the period for which financial statements are presented and the date on which the same will actually be made available to the public.
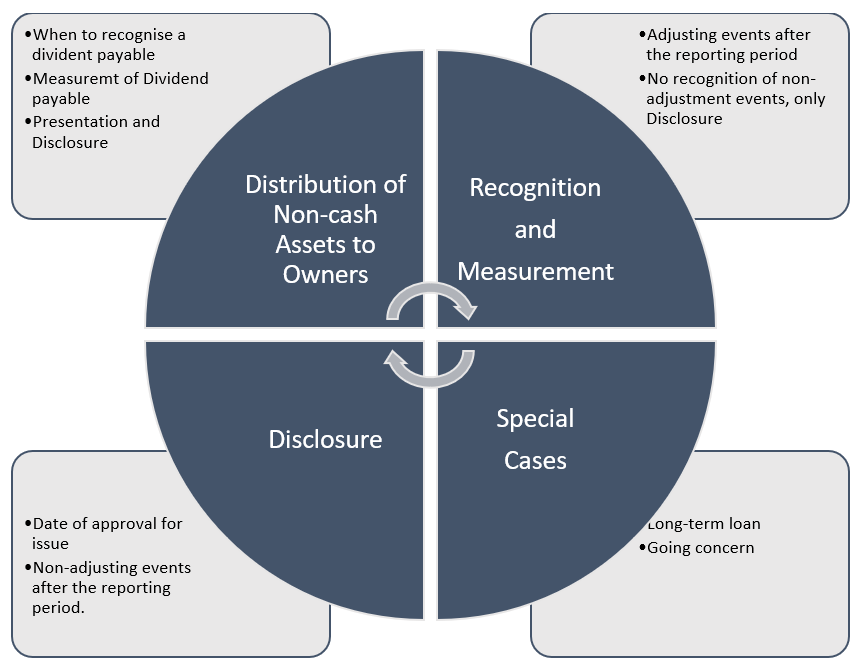
- Event occurring after the reporting period are defined as ‘events which occur between the end of the reporting date and the date when the financial statements are approved by the Board of Directors in case of a company’ and ‘by the corresponding authority in case of any other entity’.
- These events may be Adjusting and Un-adjusting.
Adjusting events: Those that provide evidence of conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period.
Non-Adjusting events: Those that are indicative of conditions that arose after the reporting period.
- Events after the reporting period include all events up to the date when the financial statements are authorized for issue, even if those events occur after the public announcement of profit or of other selected financial information.
The objective of Ind-AS 10 is to prescribe:
- The disclosures that an entity should give about the date when the financial statements were approved for issue and about events after the reporting.
- When an entity should adjust its financial statements for events after the reporting period.
Adjusting events:
(a) An entity should adjust its financial statements for events after the reporting date that provide further evidence of conditions that existed at the reporting date.
(b) Notwithstanding anything about adjusting or non-adjusting events, where there is a breach of a material provision of a long-term loan arrangement on or before the end of the reporting period with the effect that the liability becomes payable on demand on the reporting date, the agreement by lender before the approval of the financial statements for issue, to not demand payment as a consequence of such breach, shall be considered as an adjusting event.
An entity shall adjust the amounts recognised in its financial statements to reflect adjusting events after the reporting period.
An entity shall not adjust the amounts recognised in its financial statements to reflect non-adjusting events after the reporting period.
However, if non-adjusting events after the reporting period are material and their non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions that users make on the basis of the financial statements, then it shall disclose the following for each material category of non-adjusting event after the reporting period:
- The nature of the event.
- An estimate of its financial effect, or a statement that such an estimate cannot be.
If an entity receives information after the reporting period about conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period, it shall update disclosures that relate to those conditions, in the light of the new information. Appendix A of Ind AS 10 provides guidance with regard to distribution of non–cash assets as dividends to owners. The Appendix prescribes that liability to pay such a dividend should be recognised when it is appropriately authorised and is no longer at the discretion of the entity. This liability should be measured at the fair value of assets to be distributed. Any difference between the carrying amount of the assets distributed and the carrying amount of the dividend payable should be recognised in profit or loss when an entity settles the dividend payable.
Dividends:
(a) If dividend to holders of equity instruments are proposed or declared after the reporting date, an entity should not recognize those dividends as liability. There is no obligation as on the reporting date.
(b) The entity would disclose if any dividend is declared or proposed after the reporting date but before the date of approval of financial statements.
(c) An enterprise may give the disclosure of proposed dividends either on the face of the balance sheet as an appropriation within equity or in the notes in accordance with Ind AS 1 “Presentation of Financial Statements”.
Going concern:
(a) An entity should not prepare its financial statements on a going concern basis if management determines after the reporting date either that it intends to liquidate the entity or to cease trading, or that it has no realistic alternatives but to do so.
(b) However, there should no longer be a requirement to adjust the financial statements where an event after the reporting date indicates that going concern assumption is not appropriate. In that case there is need for fundamental change in the basis of accounting rather than adjustment.
(c) Ind-AS 1 specifies required disclosure if:
- The financial statements are not prepared on a going concern basis.
- Management is aware of material uncertainties related to events or conditions that may cast significant doubt upon the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern. The events or conditions requiring disclosure may arise after the reporting period.
Events after the Reporting Period
Events after the reporting period are those events, favourable and unfavourable, that occur between the end of the reporting period and the date when the financial statements are approved.
Mandatory exceptions:
(a) An entity’s estimates in accordance with Ind AS at the date of transition to Ind AS shall be consistent with estimates made for the same date in accordance with previous GAAP (after adjustments to reflect any difference in accounting policies), unless there is objective evidence that those estimates were in error.
(b) An entity may need to make estimates in accordance with Ind AS at the date of transition to Ind AS that were not required at that date under previous GAAP. To achieve consistency with Ind AS 10, those estimates in accordance with Ind AS shall reflect conditions that existed at the date of transition to Ind AS. In particular, estimates at the date of transition to Ind AS of market prices, interest rates or foreign exchange rates shall reflect market conditions at that date.