Preference Shares are a type of share capital that provides shareholders a preferential right over equity shareholders in two key aspects: (1) Receiving dividends at a fixed rate before equity shareholders, and (2) Repayment of capital during winding up of the company. They usually do not carry voting rights, except in special cases. Preference shares may be cumulative, non-cumulative, redeemable, or convertible. They are considered a hybrid security, combining features of both equity and debt, offering stability to investors and flexible financing to companies.
Valuation of Preference Shares:
Valuation depends on whether preference shares are irredeemable or redeemable.
A. Irredeemable Preference Shares
-
These shares have no maturity date; holders get a fixed dividend forever.
-
Value is calculated as the present value of perpetual dividends.
Formula:
Value of Irredeemable Preference Share = Annual Preference Dividend / Required Rate of Return
B. Redeemable Preference Shares
-
These shares are repayable after a fixed period (say 5 or 10 years).
-
Value is based on the present value of dividends for n years plus present value of redemption value.
Formula:
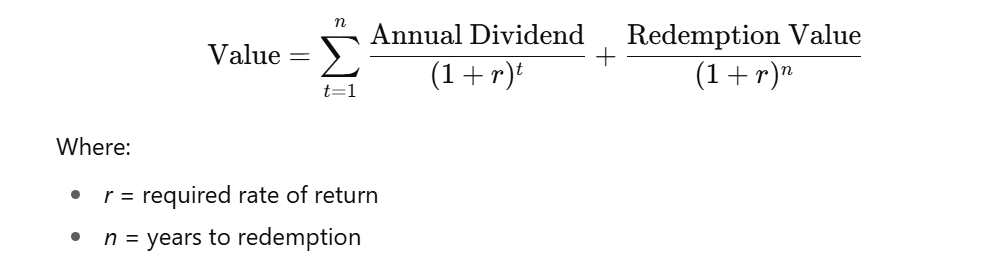
Need of Valuation of Preference Shares:
-
Investment Decision-Making
Valuation of preference shares helps investors decide whether to buy, hold, or sell such securities. Since preference shareholders receive fixed dividends and priority over equity shareholders, knowing the fair value ensures they do not overpay or undervalue their investment. By comparing the intrinsic value with the market price, investors can judge potential returns and risks. This process builds confidence in investment decisions, especially for risk-averse investors who prefer stable returns rather than uncertain equity dividends.
-
Corporate Financing Decisions
Companies issue preference shares as a source of capital, combining features of both debt and equity. Before issuing or redeeming such shares, firms must know their value to ensure cost-effective financing. Valuation helps management compare preference shares with other funding sources like debentures or equity. It also influences dividend payout policies and redemption strategies. Thus, correct valuation ensures balanced capital structure, reduces financing costs, and maintains investor trust, which is essential for smooth business operations and long-term sustainability.
-
Regulatory and Legal Requirements
Valuation of preference shares becomes necessary during mergers, acquisitions, liquidation, or restructuring of a company. Laws and accounting standards often require that shareholders, including preference shareholders, receive fair value for their holdings. Accurate valuation ensures compliance with statutory provisions and prevents disputes among stakeholders. It also helps in calculating compensation payable to preference shareholders when the company decides to redeem or convert their shares. Thus, valuation ensures transparency, fairness, and legal compliance in corporate financial transactions and governance.
-
Redemption and Conversion Decisions
Preference shares are often redeemable after a fixed period or convertible into equity shares. In both cases, valuation plays a vital role. For redemption, it helps determine the repayment amount and its impact on company finances. For conversion, valuation ensures fair exchange ratios between preference and equity shares, avoiding shareholder conflicts. This process safeguards the interests of both the company and investors. Therefore, proper valuation ensures smooth redemption or conversion, maintains fairness, and supports effective long-term financial planning.
Share this:
- Share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Share on Pocket (Opens in new window) Pocket
- Share on Threads (Opens in new window) Threads
- More