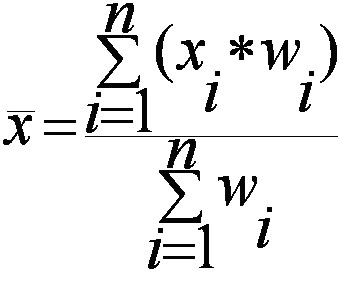Sampling and Sampling Distribution
Sample design is the framework, or road map, that serves as the basis for the selection of a survey sample and affects many other important aspects of a survey as well. In a broad context, survey researchers are interested in obtaining some type of information through a survey for some population, or universe, of interest. One must define a sampling frame that represents the population of interest, from which a sample is to be drawn. The sampling frame may be identical to the population, or it may be only part of it and is therefore subject to some under coverage, or it may have an indirect relationship to the population.
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals, items, or observations from a larger population to analyze and draw conclusions about the entire group. It is essential in statistics when studying the entire population is impractical, time-consuming, or costly. Sampling can be done using various methods, such as random, stratified, cluster, or systematic sampling. The main objectives of sampling are to ensure representativeness, reduce costs, and provide timely insights. Proper sampling techniques enhance the reliability and validity of statistical analysis and decision-making processes.
Steps in Sample Design
While developing a sampling design, the researcher must pay attention to the following points:
- Type of Universe:
The first step in developing any sample design is to clearly define the set of objects, technically called the Universe, to be studied. The universe can be finite or infinite. In finite universe the number of items is certain, but in case of an infinite universe the number of items is infinite, i.e., we cannot have any idea about the total number of items. The population of a city, the number of workers in a factory and the like are examples of finite universes, whereas the number of stars in the sky, listeners of a specific radio programme, throwing of a dice etc. are examples of infinite universes.
- Sampling unit:
A decision has to be taken concerning a sampling unit before selecting sample. Sampling unit may be a geographical one such as state, district, village, etc., or a construction unit such as house, flat, etc., or it may be a social unit such as family, club, school, etc., or it may be an individual. The researcher will have to decide one or more of such units that he has to select for his study.
- Source list:
It is also known as ‘sampling frame’ from which sample is to be drawn. It contains the names of all items of a universe (in case of finite universe only). If source list is not available, researcher has to prepare it. Such a list should be comprehensive, correct, reliable and appropriate. It is extremely important for the source list to be as representative of the population as possible.
- Size of Sample:
This refers to the number of items to be selected from the universe to constitute a sample. This a major problem before a researcher. The size of sample should neither be excessively large, nor too small. It should be optimum. An optimum sample is one which fulfills the requirements of efficiency, representativeness, reliability and flexibility. While deciding the size of sample, researcher must determine the desired precision as also an acceptable confidence level for the estimate. The size of population variance needs to be considered as in case of larger variance usually a bigger sample is needed. The size of population must be kept in view for this also limits the sample size. The parameters of interest in a research study must be kept in view, while deciding the size of the sample. Costs too dictate the size of sample that we can draw. As such, budgetary constraint must invariably be taken into consideration when we decide the sample size.
- Parameters of interest:
In determining the sample design, one must consider the question of the specific population parameters which are of interest. For instance, we may be interested in estimating the proportion of persons with some characteristic in the population, or we may be interested in knowing some average or the other measure concerning the population. There may also be important sub-groups in the population about whom we would like to make estimates. All this has a strong impact upon the sample design we would accept.
- Budgetary constraint:
Cost considerations, from practical point of view, have a major impact upon decisions relating to not only the size of the sample but also to the type of sample. This fact can even lead to the use of a non-probability sample.
- Sampling procedure:
Finally, the researcher must decide the type of sample he will use i.e., he must decide about the technique to be used in selecting the items for the sample. In fact, this technique or procedure stands for the sample design itself. There are several sample designs (explained in the pages that follow) out of which the researcher must choose one for his study. Obviously, he must select that design which, for a given sample size and for a given cost, has a smaller sampling error.
Types of Samples

- Probability Sampling (Representative samples)
Probability samples are selected in such a way as to be representative of the population. They provide the most valid or credible results because they reflect the characteristics of the population from which they are selected (e.g., residents of a particular community, students at an elementary school, etc.). There are two types of probability samples: random and stratified.
- Random Sample
The term random has a very precise meaning. Each individual in the population of interest has an equal likelihood of selection. This is a very strict meaning you can’t just collect responses on the street and have a random sample.
The assumption of an equal chance of selection means that sources such as a telephone book or voter registration lists are not adequate for providing a random sample of a community. In both these cases there will be a number of residents whose names are not listed. Telephone surveys get around this problem by random-digit dialling but that assumes that everyone in the population has a telephone. The key to random selection is that there is no bias involved in the selection of the sample. Any variation between the sample characteristics and the population characteristics is only a matter of chance.
- Stratified Sample
A stratified sample is a mini-reproduction of the population. Before sampling, the population is divided into characteristics of importance for the research. For example, by gender, social class, education level, religion, etc. Then the population is randomly sampled within each category or stratum. If 38% of the population is college-educated, then 38% of the sample is randomly selected from the college-educated population.
Stratified samples are as good as or better than random samples, but they require fairly detailed advance knowledge of the population characteristics, and therefore are more difficult to construct.
- Non-probability Samples (Non-representative samples)
As they are not truly representative, non-probability samples are less desirable than probability samples. However, a researcher may not be able to obtain a random or stratified sample, or it may be too expensive. A researcher may not care about generalizing to a larger population. The validity of non-probability samples can be increased by trying to approximate random selection, and by eliminating as many sources of bias as possible.
- Quota Sample
The defining characteristic of a quota sample is that the researcher deliberately sets the proportions of levels or strata within the sample. This is generally done to insure the inclusion of a particular segment of the population. The proportions may or may not differ dramatically from the actual proportion in the population. The researcher sets a quota, independent of population characteristics.
Example: A researcher is interested in the attitudes of members of different religions towards the death penalty. In Iowa a random sample might miss Muslims (because there are not many in that state). To be sure of their inclusion, a researcher could set a quota of 3% Muslim for the sample. However, the sample will no longer be representative of the actual proportions in the population. This may limit generalizing to the state population. But the quota will guarantee that the views of Muslims are represented in the survey.
- Purposive Sample
A purposive sample is a non-representative subset of some larger population, and is constructed to serve a very specific need or purpose. A researcher may have a specific group in mind, such as high level business executives. It may not be possible to specify the population they would not all be known, and access will be difficult. The researcher will attempt to zero in on the target group, interviewing whoever is available.
- Convenience Sample
A convenience sample is a matter of taking what you can get. It is an accidental sample. Although selection may be unguided, it probably is not random, using the correct definition of everyone in the population having an equal chance of being selected. Volunteers would constitute a convenience sample.
Non-probability samples are limited with regard to generalization. Because they do not truly represent a population, we cannot make valid inferences about the larger group from which they are drawn. Validity can be increased by approximating random selection as much as possible, and making every attempt to avoid introducing bias into sample selection.
Sampling Distribution
Sampling Distribution is a statistical concept that describes the probability distribution of a given statistic (e.g., mean, variance, or proportion) derived from repeated random samples of a specific size taken from a population. It plays a crucial role in inferential statistics, providing the foundation for making predictions and drawing conclusions about a population based on sample data.
Concepts of Sampling Distribution
A sampling distribution is the distribution of a statistic (not raw data) over all possible samples of the same size from a population. Commonly used statistics include the sample mean (Xˉ\bar{X}), sample variance, and sample proportion.
Purpose:
It allows statisticians to estimate population parameters, test hypotheses, and calculate probabilities for statistical inference.
Shape and Characteristics:
-
- The shape of the sampling distribution depends on the population distribution and the sample size.
- For large sample sizes, the Central Limit Theorem states that the sampling distribution of the mean will be approximately normal, regardless of the population’s distribution.
Importance of Sampling Distribution
- Facilitates Statistical Inference:
Sampling distributions are used to construct confidence intervals and perform hypothesis tests, helping to infer population characteristics.
- Standard Error:
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution, called the standard error, quantifies the variability of the sample statistic. Smaller standard errors indicate more reliable estimates.
- Links Population and Samples:
It provides a theoretical framework that connects sample statistics to population parameters.
Types of Sampling Distributions
- Distribution of Sample Means:
Shows the distribution of means from all possible samples of a population.
- Distribution of Sample Proportions:
Represents the proportion of a certain outcome in samples, used in binomial settings.
- Distribution of Sample Variances:
Explains the variability in sample data.
Example
Consider a population of students’ test scores with a mean of 70 and a standard deviation of 10. If we repeatedly draw random samples of size 30 and calculate the sample mean, the distribution of those means forms the sampling distribution. This distribution will have a mean close to 70 and a reduced standard deviation (standard error).