Selection is the process of choosing the most suitable candidates from a pool of applicants for a specific job role within an organization. It involves assessing candidates’ qualifications, skills, experience, and cultural fit to determine their potential to succeed in the role. The selection process typically includes steps such as screening resumes, conducting interviews, administering tests, and performing background checks. The goal of selection is to identify candidates who not only meet the job requirements but also align with the organization’s values, ensuring long-term success and reducing turnover.
Finding the interested candidates who have submitted their profiles for a particular job is the process of recruitment, and choosing the best and most suitable candidates among them is the process of selection. It results in elimination of unsuitable candidates. It follows scientific techniques for the appropriate choice of a person for the job.
The recruitment process has a wide coverage as it collects the applications of interested candidates, whereas the selection process narrows down the scope and becomes specific when it selects the suitable candidates.
Stone defines, ‘Selection is the process of differentiating between applicants in order to identify (and hire) those with a greater likelihood of success in a job’.
Steps Involved in Selection Procedure:
A scientific and logical selection procedure leads to scientific selection of candidates. The criterion finalized for selecting a candidate for a particular job varies from company to company.
Therefore, the selection procedure followed by different organizations, many times, becomes lengthy as it is a question of getting the most suitable candidates for which various tests are to be done and interviews to be taken. The procedure for selection should be systematic so that it does not leave any scope for confusions and doubts about the choice of the selected candidate (Figure 5.6).
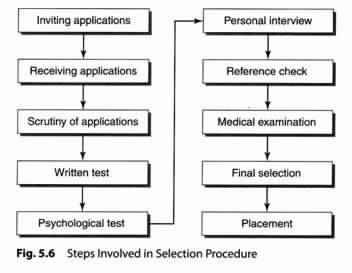
1. Inviting applications:
The prospective candidates from within the organization or outside the organization are called for applying for the post. Detailed job description and job specification are provided in the advertisement for the job. It attracts a large number of candidates from various areas.
2. Receiving applications:
Detailed applications are collected from the candidates which provide the necessary information about personal and professional details of a person. These applications facilitate analysis and comparison of the candidates.
3. Scrutiny of applications:
As the limit of the period within which the company is supposed to receive applications ends, the applications are sorted out. Incomplete applications get rejected; applicants with un-matching job specifications are also rejected.
4. Written tests:
As the final list of candidates becomes ready after the scrutiny of applications, the written test is conducted. This test is conducted for understanding the technical knowledge, attitude and interest of the candidates. This process is useful when the number of applicants is large.
Many times, a second chance is given to candidates to prove themselves by conducting another written test.
5. Psychological tests:
These tests are conducted individually and they help for finding out the individual quality and skill of a person. The types of psychological tests are aptitude test, intelligence test, synthetic test and personality test
6. Personal interview:
Candidates proving themselves successful through tests are interviewed personally. The interviewers may be individual or a panel. It generally involves officers from the top management.
The candidates are asked several questions about their experience on another job, their family background, their interests, etc. They are supposed to describe their expectations from the said job. Their strengths and weaknesses are identified and noted by the interviewers which help them to take the final decision of selection.
7. Reference check:
Generally, at least two references are asked for by the company from the candidate. Reference check is a type of crosscheck for the information provided by the candidate through their application form and during the interviews.
8. Medical examination:
Physical strength and fitness of a candidate is must before they takes up the job. In-spite of good performance in tests and interviews, candidates can be rejected on the basis of their ill health.
9. Final selection:
At this step, the candidate is given the appointment letter to join the organization on a particular date. The appointment letter specifies the post, title, salary and terms of employment. Generally, initial appointment is on probation and after specific time period it becomes permanent.
10. Placement:
This is a final step. A suitable job is allocated to the appointed candidate so that they can get the whole idea about the nature of the job. They can get adjusted to the job and perform well in future with all capacities and strengths.