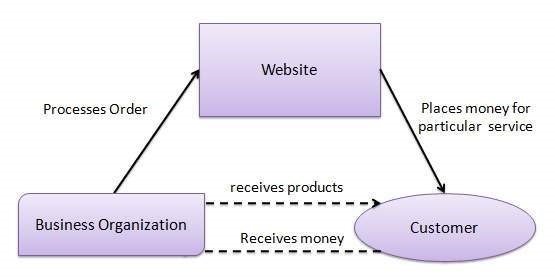
In this model, a consumer approaches a website showing multiple business organizations for a particular service. The consumer places an estimate of amount he/she wants to spend for a particular service. For example, the comparison of interest rates of personal loan/car loan provided by various banks via websites. A business organization who fulfills the consumer’s requirement within the specified budget, approaches the customer and provides its services.
Consumer-to-business (C2B) is a business model in which consumers (individuals) create value and businesses consume that value. For example, when a consumer writes reviews or when a consumer gives a useful idea for new product development then that consumer is creating value for the business if the business adopts the input. In the C2B model, a reverse auction or demand collection model, enables buyers to name or demand their own price, which is often binding, for a specific good or service. Inside of a consumer to business market the roles involved in the transaction must be established and the consumer must offer something of value to the business.
Another form of C2B is the electronic commerce business model in which consumers can offer products and services to companies, and the companies pay the consumers. This business model is a complete reversal of the traditional business model in which companies offer goods and services to consumers (business-to-consumer = B2C). We can see the C2B model at work in blogs or internet forums in which the author offers a link back to an online business thereby facilitating the purchase of a product (like a book on Amazon.com), for which the author might receive affiliate revenues from a successful sale. Elance was the first C2B model e-commerce site.
C2B is a kind of economic relationship that is qualified as an inverted business type. The advent of the C2B scheme is due to:
- The internet connecting large groups of people to a bidirectional network; the large traditional media outlets are one-directional relationships whereas the internet is bidirectional.
- Decreasing costs of technology; individuals now have access to technologies that were once only available to large companies (digital printing and acquisition technology, high-performance computers, and powerful software).
Positives and Negatives
Nowadays people have smartphones or connect to the internet through personal tablets/computers daily allowing consumers to engage with brands online. According to Katherine Arline, in traditional consumer-to-business models companies would promote goods and services to consumers, but a shift has occurred to allow consumers to be the driving force behind a transaction. To the consumers benefit, reverse auctions occur in consumer to business markets allowing the consumer to name their price for a product or service.
A consumer can also provide value to a business by offering to promote a business products on a consumers blog or social media platforms. Businesses are provided value through their consumers and vice versa.
Businesses gain in C2B from the consumers willingness to negotiate price, contribute data, or market to the company. Consumers profit from direct payment of the reduced-price goods and services and the flexibility of the transaction the C2B market created. Consumer to business markets have their downfall as well. C2B is still a relatively new business practice and has not been fully studied.
Data Aggregation
Aggregation of data is a common C2B practice done with many internet corporations. In this instance, the consumer is creating the value of personal information and data to better target them to the correct advertisers. Businesses such as Facebook, Twitter, and others utilize this information in an effort to facilitate their B2B transactions with advertisers. Most of these systems cannot be fully utilized without B2C or B2B transactions, as C2B is usually the facilitator of these.
3 thoughts on “Consumer to Business (C2B) business Model”