Channel design decisions are critical because they determine a product’s market presence and buyer’s accessibility to the product. Channel decisions have additional strategic significance because they entail long-term commitments. It is usually easier to change prices or promotion than to change marketing channels.
-
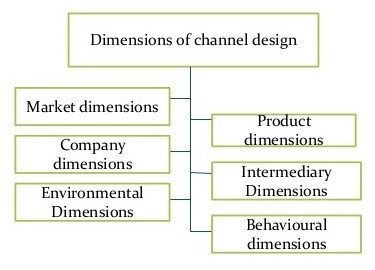
Market dimensions
It focuses on customer( market) orientation. In developing and adapting the marketing mix, then, marketing managers should take their basic cues from the needs and wants to the target markets at which they are aiming. Four basic sub categories of market variables are particularly important in influencing channel structure. They are:
- Market geography
- Market size
- Market density
- Market Behaviour
-
Product Dimension
Product variables are another important category to consider in evaluating alternative channel structures. Some of the most important product variables are as follows:
- Bulk and weight
- Perishability
- Unit value
- Technical versus non- technical
- Newness
-
Company dimensions
The most important company variables affecting channel design are:
- Size
- Financial capacity
- Managerial Expertise
- Objectives and Strategies
-
Intermediary Dimensions
The key intermediary variables related to channel structure are:
- Availability
- Cost
- Services
-
Environment dimension
Environmental variables may affect all aspects of channel development and management. Economic, sociocultural, competitive, technological, and legal environmental forces can have a significant impact of environmental forces is one of the more common reasons for marketing channel design decisions.
-
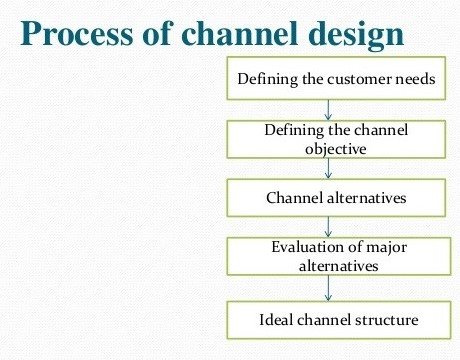
Defining the customer needs
In designing the market channel, the marketer must understand the service output levels its target customer want. It is essential to capture customer requirements while designing marketing channel. It includes the following:
- Product information
- Product customization
- Product quality assurance
- Lot size Product variety
- Spatial convenience / availability
- Waiting and delivery time After sales service
- Logistics
-
Defining channel objective
The channel objective vary with product characteristics:
- Perishable products requires more direct marketing
- Bulky products, such as building materials, require channels that minimize the shipping distance and amount of handling.
- Non- standard products, such as custom-built machinary and specialised business forms, are sold directly by company sales representatives.
- High- unit- value products such as generators and turbines are often sold through a company sales force rather than intermediaries.
-
Channel alternative
A company looks at alternatives for its distribution channel after it has decided on the targeted customers and the customer service deliverables it desires from its channel partners to reach these customers. At the time of deciding the company will scan for:
Type of intermediaries
- Distributors or re-distribution stockiest
- Carrying and forwarding agents
- Logistics service providers.
- Manufacturer’s agents, stockist, guarantors
- Financing agencies
- Wholesalers and semi wholsalers
- Retailers and service centres.
- Number of intermediaries.
- Cost of the channel system.
- Terms and responsibility of channel members.
-
Evaluation of major alternative
The major problem before the producer is to decide which of the alternatives would be best satisfy the long term objectives of the firm taking in view the factors which would affect the channel decision. For this purpose, each alternative must be rated against economic; control and adequate criteria:
- Economic Criteria
- Control Criteria
- Adaptive Criteria
-
Ideal channel structure
With the completion of forgoing steps, the number of alternatives would have narrowed down considerably. The firm must evaluate design and choose the best among them.