Information, as required at different levels of management can be classified as operational, tactical and strategic.
-
Strategic information
While the operational information is needed to find out how the given activity can be performed better, strategic information is needed for making choices among the business options.
The strategic information helps in identifying and evaluating these options so that a manager makes informed choices which are different from the competitors and the limitations of what the rivals are doing or planning to do. Such choices are made by leaders only.
Strategic information is used by managers to define goals and priorities, initiate new programmes and develop policies for acquisition and use of corporate resources. For example, information regarding the long-term needs of funds for on-going and future projects of the company may be used by top level managers in taking decision regarding going public or approaching financial institutions for term loan.
Strategic information is predictive in nature, relies heavily on external sources of data, has a long-term perspective, and is mostly in summary form. It may sometimes include ‘what if’ scenarios. However, the strategic information is not only external information.
For long, it was believed that strategic information are basically information regarding the external environment. However, it is now well recognised that the internal factors are equally responsible for success or failures of strategies and thus, internal information is also required for strategic decision making.
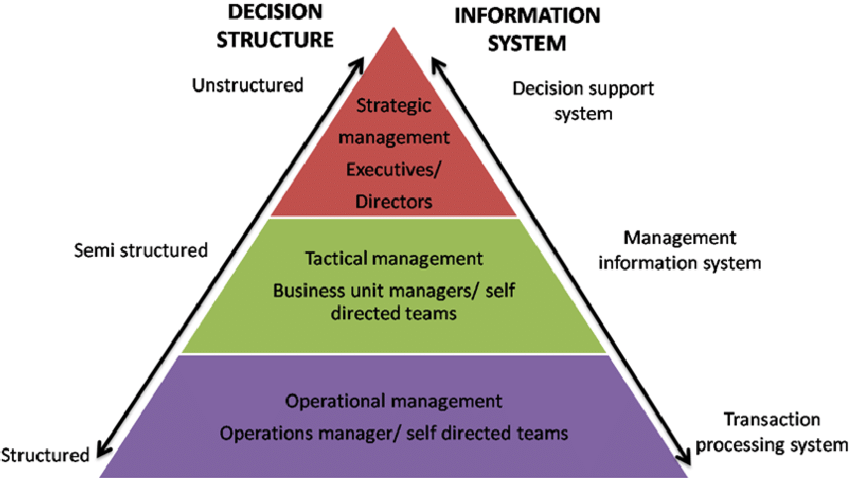
Figure represents the types of information required at different levels of managerial hierarchy.
It may be remembered that each type of information has its role to play in managerial effectiveness. Each type of information is needed with varying degree by the managers at all levels. Thus, a part of operational information may be used even by the chief executive officer of a company.
The difference lies in the proportion of each type of information in the total information needs of managers at different levels of managerial hierarchy.
-
Tactical information
Tactical information helps middle level managers allocating resources and establishing controls to implement the top level plans of the organisation. For example, information regarding the alternative sources of funds and their uses in the short run, opportunities for deployment of surplus funds in short- term securities, etc. may be required at the middle levels of management.
The tactical information is generally predictive, focusing on short-term trends. It may be partly current and partly historical, and may come from internal as well as external sources.
-
Operational information
Operational information relates to the day-to-day operations of the organization and thus, is useful in exercising control over the operations that are repetitive in nature. Since such activities are controlled at lower levels of management, operational information is needed by the lower management.
For example, the information regarding the cash position on day-to-day basis is monitored and controlled at the lower levels of management. Similarly, in marketing function, daily and weekly sales information is used by lower level manager to monitor the performance of the sales force.
It may be noted that operational information pertains to activities that are easily measurable by specific standards. The operational information mainly relates to current and historical performance, and is based primarily on internal sources of data. The predictive element in operational information is quite low and if at all it is there, it has a short term horizon.