Conjoint Analysis is a statistical technique used in market research to understand consumer preferences and the value they place on different product features or attributes. It involves presenting respondents with various product profiles that combine different feature levels, allowing researchers to determine which combinations of attributes drive purchasing decisions. By analyzing the trade-offs consumers are willing to make, businesses can identify the optimal product features, pricing, and configurations that maximize customer satisfaction and market share. Conjoint analysis helps companies design products that align with consumer desires and optimize their offerings in a competitive market.
Steps of Conjoint Analysis:
-
Define the Objective
The first step in conjoint analysis is to clearly define the research objective. This involves understanding what the business seeks to achieve from the analysis, such as determining the most important product features, identifying market segments, or setting optimal pricing strategies. The objective sets the direction for the rest of the process, ensuring that the analysis is focused and relevant.
-
Select the Attributes and Levels
The next step is to identify the key product attributes (features or characteristics) that influence consumer decisions. These can include factors such as price, color, size, functionality, brand, or service offerings. For each attribute, different levels must be defined. For example, the “price” attribute could have levels like “$10”, “$20”, and “$30”. It’s essential to select a manageable number of attributes and levels, as too many may make the analysis complex and overwhelming for respondents.
-
Design the Product Profiles
Once the attributes and levels are identified, the next step is to design the product profiles, which are hypothetical combinations of the attributes and their levels. These profiles represent the different product or service options that consumers will evaluate. The design process often involves creating a set of profiles that represent realistic and diverse combinations, ensuring that all important attribute-level combinations are tested.
-
Develop the Survey Questionnaire
A survey questionnaire is created to collect consumer preferences. Respondents are presented with different product profiles and asked to evaluate or rank them based on their preferences. There are several techniques for this, including choice-based conjoint (CBC) or traditional ratings and rankings. The survey should be designed to be clear, concise, and engaging to ensure accurate responses and minimize respondent fatigue.
-
Collect Data
The survey is then administered to the target audience. Depending on the study, this could be done through various channels such as online surveys, phone interviews, or focus groups. It’s important to collect a sufficient amount of data from a representative sample to ensure the results are statistically valid and reliable. Respondents should be carefully selected based on relevant demographic characteristics to match the target market for the product.
-
Analyze the Data
Once the data is collected, it is analyzed using specialized statistical techniques to determine the importance of each attribute and the utility values of different levels. The analysis reveals how consumers perceive the trade-offs between different attributes and how each attribute influences their decision-making. The output from the analysis includes part-worth utilities (values representing the relative importance of each attribute level) and a rank order of the attributes.
-
Interpret the Results
The next step is to interpret the results. This involves examining the utility values to understand the relative importance of different attributes and identifying which combination of attributes is most likely to drive consumer preference. The results can also be used to estimate the market share of various product configurations and predict consumer behavior under different conditions, such as changes in price or features.
-
Make Business Decisions
Finally, the insights gained from the conjoint analysis are used to make informed business decisions. This could involve designing products that align with consumer preferences, optimizing pricing strategies, or adjusting marketing campaigns. Conjoint analysis helps businesses tailor their offerings to better meet consumer needs and maximize their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Uses of Conjoint Analysis:
-
Product Design and Feature Selection
Conjoint analysis helps businesses determine which product features are most important to consumers. By evaluating various feature combinations, companies can understand which attributes (e.g., color, size, functionality) are most valued and make informed decisions about which features to prioritize in new product designs. This ensures that the product meets market demand and enhances customer satisfaction.
-
Pricing Strategy Development
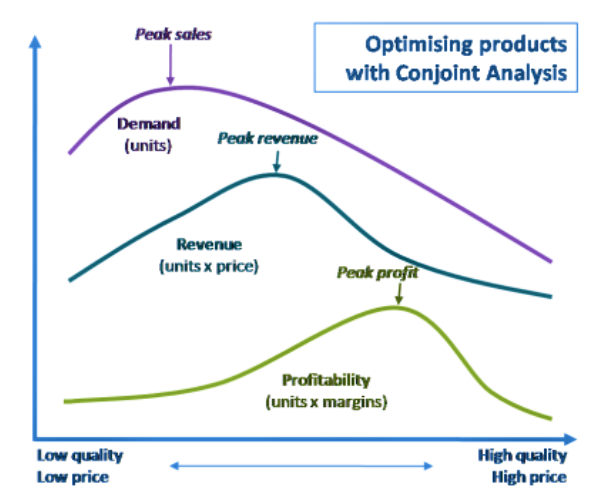
Conjoint analysis is instrumental in developing effective pricing strategies. By assessing how much consumers are willing to pay for different product features, businesses can find the optimal price point that maximizes both sales volume and profitability. It helps to evaluate the impact of price changes on demand and consumer preferences, aiding in setting competitive yet profitable prices.
-
Market Segmentation
One of the key applications of conjoint analysis is market segmentation. It allows businesses to segment their target market based on differing preferences and purchasing behaviors. By analyzing consumer responses to various product profiles, companies can identify distinct consumer segments and tailor their marketing strategies to each segment’s unique needs and preferences.
-
New Product Development
When developing new products, businesses can use conjoint analysis to test different product configurations before launch. By simulating potential product offerings and evaluating consumer reactions, companies can predict the success of the product in the market. It also helps to identify unmet needs in the market, allowing for the creation of innovative products that stand out.
-
Competitive Analysis
Conjoint analysis helps businesses understand how their products compare to competitors’ offerings in terms of features, pricing, and consumer preferences. By analyzing the relative importance of various product attributes, businesses can gain insights into how they can differentiate their products to outperform competitors. It helps companies fine-tune their competitive strategies for better positioning in the market.
-
Brand Positioning
Conjoint analysis is valuable in refining brand positioning strategies. By evaluating consumer preferences for different product features associated with specific brands, businesses can determine which attributes are most closely tied to their brand image. This helps in developing marketing messages that resonate with the target audience and strengthen brand positioning in the market.
-
Forecasting Consumer Behavior
Conjoint analysis can be used to predict how changes in product features, pricing, or availability will affect consumer choices. By simulating various market conditions, companies can forecast how customers will respond to modifications in product attributes. This predictive capability aids in planning product launches, marketing campaigns, and other strategic decisions with greater accuracy.
-
Portfolio Optimization
Conjoint analysis is often used to optimize product portfolios by evaluating the performance of different product configurations. It helps companies determine which products or features to include in their offerings and which ones to discontinue. By analyzing the trade-offs consumers make between different products and features, companies can ensure they focus on the most profitable and desirable options.