Choice of Strategy refers to the process of selecting the most appropriate strategic option that aligns with an organization’s goals, internal capabilities, and external environment. It involves evaluating various alternatives based on their feasibility, acceptability, and suitability. The chosen strategy should provide a clear path to competitive advantage, sustainability, and value creation. This decision is influenced by factors such as market trends, resource availability, stakeholder expectations, and risk assessment. Strategic choice acts as a bridge between strategic analysis and implementation, ensuring that the organization commits to a coherent direction that supports long-term growth and performance.
Importance of Strategic Choices:
-
Provides Direction and Focus
Strategic choices give an organization a clear direction by defining where it is headed and how it plans to get there. By selecting a particular path from various alternatives, companies can set specific goals and objectives, enabling focused efforts and resource alignment. This clarity ensures that every department and employee understands their role in achieving the overall strategy. Without a well-defined strategic choice, organizations may drift, waste resources, or pursue conflicting priorities. Thus, it brings unity and clarity in the decision-making process, helping avoid confusion and inefficiency.
-
Enhances Competitive Advantage
Choosing the right strategy allows an organization to position itself effectively in the market. Whether it’s through cost leadership, differentiation, or niche focus, strategic choices help build and sustain a competitive advantage. These choices enable the company to serve customers better than its rivals by offering greater value or lower prices. A strong strategic position can create brand loyalty, reduce threats from competitors, and increase profitability. Strategic choices also guide how an organization responds to market forces and competitor actions, keeping it one step ahead in a dynamic environment.
-
Facilitates Optimal Resource Allocation
Every organization operates with limited resources. Strategic choices help allocate financial, human, and technological resources to areas with the highest strategic impact. By identifying and focusing on priority activities, businesses avoid spreading resources too thin or investing in less impactful areas. This ensures better returns on investment and improves operational efficiency. Strategic choices also assist in budget planning, manpower distribution, and capacity building, ensuring that resources are aligned with long-term goals and not wasted on short-term or uncoordinated efforts.
-
Aids in Risk Management
Strategic choices involve evaluating and selecting options based on their risks and potential returns. This helps organizations anticipate possible threats and prepare mitigation strategies in advance. By understanding the risks associated with different strategic paths—such as entering a new market or launching a new product—companies can make informed decisions that minimize uncertainty. Strategic planning also builds organizational resilience by ensuring that backup plans and flexible responses are in place in case of unexpected disruptions or changes in the external environment.
-
Encourages Long-Term Thinking
The process of making strategic choices moves an organization beyond day-to-day operations and encourages long-term planning. It forces leadership to think about where the organization wants to be in five, ten, or twenty years, and how to get there. This mindset is essential for sustainability, innovation, and growth. Without long-term thinking, organizations may make reactive decisions that bring short-term gains but compromise future success. Strategic choices ensure that present actions are connected to future outcomes, supporting continuous progress and adaptability.
-
Improves Stakeholder Confidence
When organizations make sound strategic choices and communicate them effectively, it boosts the confidence of stakeholders—such as investors, employees, customers, and business partners. A clear strategy signals that the company is well-managed, goal-oriented, and prepared to deal with challenges. It helps attract investment, retain talent, and build trust among partners and customers. Stakeholders are more likely to support a company that has a clear vision and a roadmap to achieve it, making strategic choice a foundation for strong relationships and organizational reputation.
Strategic Choice Process:
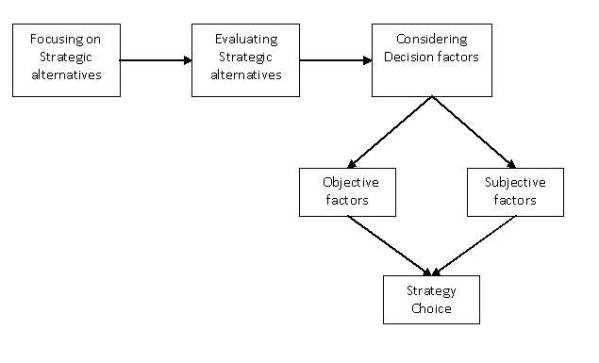
-
Identifying Strategic Options
The strategic choice process begins with identifying all viable options available to the organization. These options may include market entry strategies, diversification, cost leadership, differentiation, mergers, or strategic alliances. They are generated through strategic analysis of internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. This stage encourages creativity and comprehensive brainstorming without premature judgment. The objective is to create a list of alternatives that align with the organization’s goals, mission, and vision while responding to the current and emerging business environment.
-
Evaluating Strategic Options
Once strategic alternatives are identified, the next step is to evaluate them critically. This involves assessing each option’s suitability (alignment with goals and environment), feasibility (resource availability), and acceptability (stakeholder expectations and risk tolerance). Tools like SWOT analysis, risk analysis, cost-benefit analysis, and decision matrices are used here. The evaluation helps in identifying options that offer the best balance between risk and return. This step is crucial in filtering out weak or impractical strategies, ensuring that the remaining alternatives are aligned with the company’s capabilities and external conditions.
-
Selecting the Best Strategy
After evaluation, the most appropriate strategy is selected based on its potential to provide competitive advantage and long-term sustainability. This choice is often influenced by factors such as market position, organizational strengths, customer needs, competitor behavior, and financial projections. The chosen strategy should be robust, adaptable, and capable of addressing future uncertainties. In many cases, a combination of strategies may be chosen to achieve multiple objectives. This selection is usually made by top management with inputs from various departments to ensure alignment and consensus across the organization.
-
Communicating the Strategic Choice
Once a strategy is selected, effective communication is essential to ensure successful implementation. This includes sharing the strategic direction with all relevant stakeholders—employees, investors, suppliers, and customers—using clear, motivating, and transparent messaging. Communication should highlight the rationale behind the choice, expected outcomes, and the role each stakeholder will play. This fosters ownership, alignment, and commitment throughout the organization. Without effective communication, even a well-chosen strategy may fail due to misunderstanding, resistance, or lack of engagement from key players in the implementation process.
-
Aligning Resources and Capabilities
Strategic choice must be followed by aligning organizational resources—financial, technological, human, and operational—to support the chosen direction. This involves setting budgets, restructuring where necessary, enhancing capabilities, and acquiring the right talent or technologies. This step ensures that the organization is strategically and operationally prepared to implement the chosen strategy effectively. It also includes aligning systems, policies, and performance metrics with strategic goals. Resource alignment is critical for turning strategic intent into practical action and achieving measurable results.
-
Monitoring and Revising the Strategy
Strategic choice is not a one-time event. It must be continuously monitored to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. Regular review mechanisms, performance tracking, and feedback systems should be established to assess progress. If there are significant changes in the internal or external environment—such as technological shifts, competitor actions, or economic downturns—the strategy may need to be revised or adjusted. Flexibility and responsiveness are key components of successful strategy execution. Monitoring ensures strategic alignment with evolving business realities and maintains organizational competitiveness.