A knowledge-based system (KBS) is a computer system which generates and utilizes knowledge from different sources, data and information. These systems aid in solving problems, especially complex ones, by utilizing artificial intelligence concepts. These systems are mostly used in problem-solving procedures and to support human learning, decision making and actions.
Knowledge-based systems are considered to be a major branch of artificial intelligence. They are capable of making decisions based on the knowledge residing in them, and can understand the context of the data that is being processed.
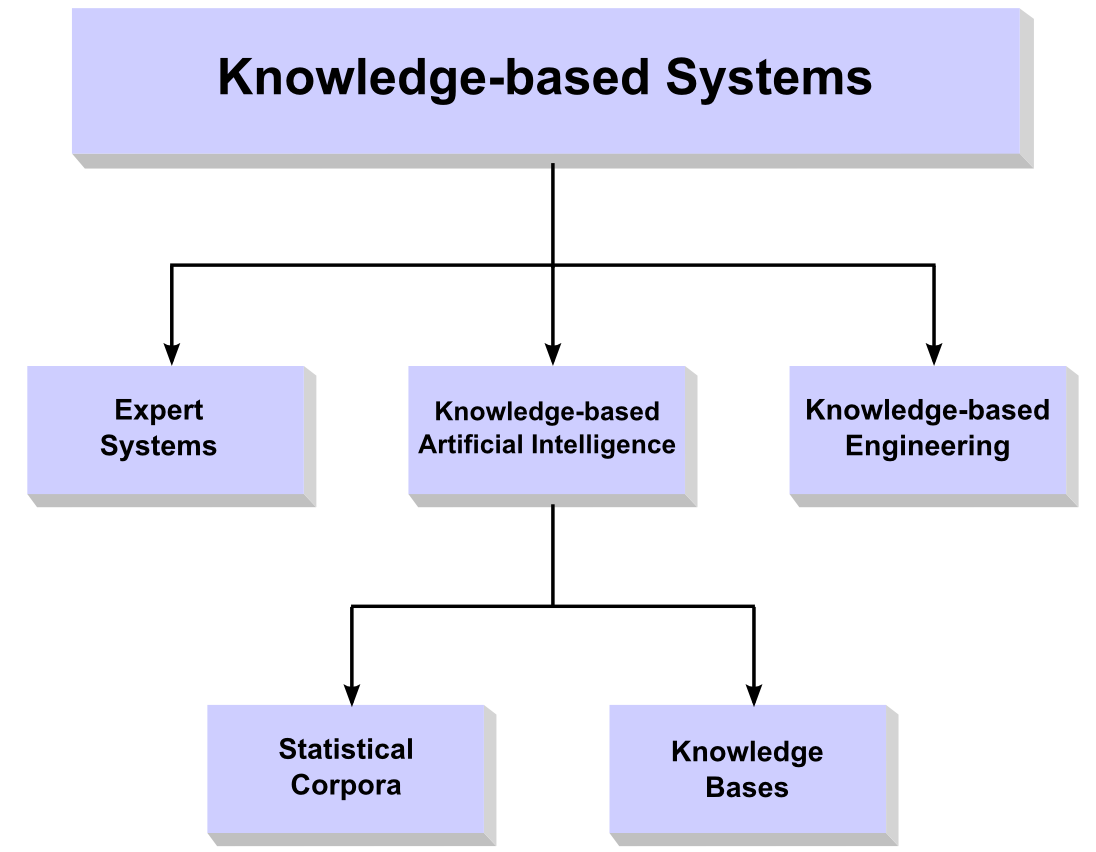
Knowledge-based systems broadly consist of an interface engine and knowledge base. The interface engine acts as the search engine, and the knowledge base acts as the knowledge repository. Learning is an essential component of knowledge-based systems and simulation of learning helps in the betterment of the systems. Knowledge-based systems can be broadly classified as CASE-based systems, intelligent tutoring systems, expert systems, hypertext manipulation systems and databases with intelligent user interface.
Compared to traditional computer-based information systems, knowledge-based systems have many advantages. They can provide efficient documentation and also handle large amounts of unstructured data in an intelligent fashion. Knowledge-based systems can aid in expert decision making and allow users to work at a higher level of expertise and promote productivity and consistency. These systems are considered very useful when expertise is unavailable, or when data needs to be stored for future usage or needs to be grouped with different expertise at a common platform, thus providing large-scale integration of knowledge. Finally, knowledge-based systems are capable of creating new knowledge by referring to the stored content.
The limitations of knowledge-based systems are the abstract nature of the concerned knowledge, acquiring and manipulating large volumes of information or data, and the limitations of cognitive and other scientific techniques.
The Evolution of Knowledge Bases
The term knowledge base was first introduced in the 1970s to distinguish from a database. At that time, databases stored flat data, transactions, and large, long-term data in computer code. By contrast, early knowledge bases aimed to provide structured knowledge that people could easily understand. This type of structured, codified information is also called an object model or ontological knowledge.
The advent of the internet changed knowledge bases considerably. It was no longer sufficient to store tables, small objects, and other straightforward, computer-coded data in computer memory. Instead, the demand for hypertext and multimedia increased, which led to more complex knowledge bases (i.e. web content management).
Today, knowledge based systems use knowledge bases, and are computer systems that aim to bridge the gaps between all the disparate types of knowledge (and file types) that people want to access.
Knowledge-Based Systems and Artificial Intelligence
While these systems are a subcategory of artificial intelligence, traditional knowledge-based systems are different in certain ways from AI. In some ways, AI is organized in a top-down, know everything system to capture and utilize statistical pattern detection methods, big data, deep learning, and data-mining. Examples of AI include approaches that involve neural network systems, which are a category of deep learning technology concentrated on pattern recognition and signal processing.
In contrast to conventional computer-based information systems, a KBS has several advantages. They provide excellent documentation while handling large quantities of unstructured data in an intelligent way. A KBS helps improve decision making and enables users to work at greater levels of expertise, productivity, and consistency. In addition, a KBS is useful when expertise is not available, or when information must be stored effectively for future use. It also provides a common platform for integrating knowledge on a large scale. Finally, a KBS is capable of generating new knowledge by using the stored data.
The architecture of a knowledge-based system is its inference engine and knowledge base. The knowledge base holds a collection of data, and the inference engine can deduce insights from the data stored in the knowledge base.
Knowledge-based systems work across a number of applications. For instance, in the medical field, a KBS can help doctors more accurately diagnose diseases. These systems are called clinical decision-support systems in the health industry. A KBS can also be used in areas as diverse as industrial equipment fault diagnosis, avalanche path analysis, and cash management.
Over the years, knowledge-based systems have been developed for a number of applications. MYCIN, for example, was an early knowledge-based system created to help doctors diagnose diseases. Healthcare has remained an important market for knowledge-based systems, which are now referred to as clinical decision-support systems in the health sciences context.
Knowledge-based systems have also been employed in applications as diverse as avalanche path analysis, industrial equipment fault diagnosis and cash management.