The need for computerization was felt in the Indian banking sector in late 1980s, in order to improve the customer service, book-keeping and MIS reporting. In 1988, Reserve Bank of India set up a Committee on computerization in banks headed by Dr. C. Rangarajan.
Banks began using Information Technology initially with the introduction of standalone PCs and migrated to Local Area Network (LAN) connectivity. With further advancement, banks adopted the Core Banking platform. Thus branch banking changed to bank banking. Core Banking Solution (CBS) enabled banks to increase the comfort feature to the customers as a promising step towards enhancing customer convenience through anywhere and anytime banking. Different Core banking platforms such as Finacle designed by Infosys, BaNCS by TCS, FLEXCUBE by i-flex, gained popularity.
The process of Computerization gained pace with the opening of the economy in 1991-92. A major driver for this change was propelled by rising competition from private and foreign banks. Several commercial banks started moving towards digital customer services to remain competitive and relevant in the race.
Banks have benefitted in several ways by adopting newer technologies. E-banking has resulted in reducing costs drastically and has helped generate revenue through various channels. As per last available information, the cost of a bank transaction on Branch Banking is estimated to be in a range of Rs.70 to Rs.75 while it is around Rs.15 to Rs.16 on ATM, Rs.2 or less on Online Banking and Rs.1 or less on Mobile Banking. The number of customer base has also increased because of the convenience in ‘Anywhere Banking’. Digitization has reduced human error. It is possible to access and analyze the data anytime enabling a strong reporting system.
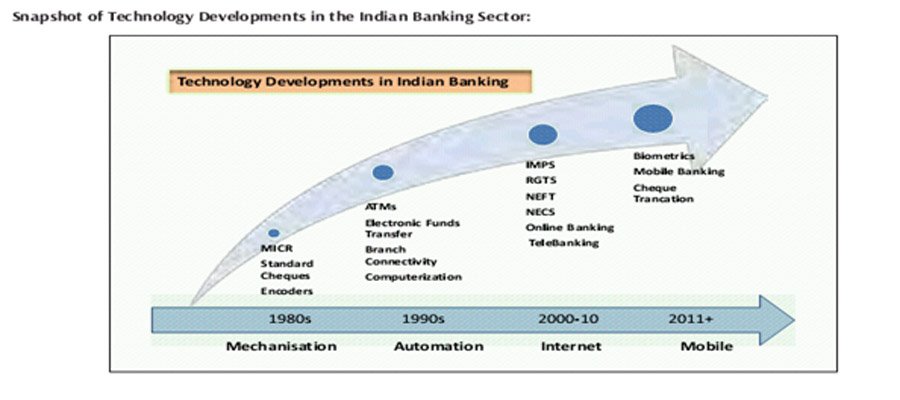
RBI has been a guiding force for the banks in forming regulations and giving recommendations to achieve various objectives. Commercial Banks in India have moved towards technology by way of Bank Mechanization and Automation with the introduction to MICR based cheque processing, Electronic Funds transfer, Inter-connectivity among bank Branches and implementation of ATM (Automated Teller Machine) Channel have resulted in the convenience of Anytime banking. Strong initiatives have been taken by the Reserve Bank of India in strengthening the Payment and Settlement systems in banks.
Technological Milestones in Indian Banks:
According to the RBI Report in 2016-17 there are 2,22,475 Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) and 25,29,141 Point of Sale devices (POS). Implementation of electronic payment system such as NEFT (National Electronic Fund Transfer), ECS (Electronic Clearing Service), RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement), Cheque Truncation System, Mobile banking system, Debit cards, Credit Cards, Prepaid cards have all gained wide acceptance in Indian banks. These are all remarkable landmarks in the digital revolution in the banking sector. Online banking has changed the face of banking and brought about a noteworthy transformation in the banking operations.
National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) is the most commonly used electronic payment method for transferring money from any bank branch to another bank in India. It operates in half hourly batches. At present there are 23 settlements.
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is primarily used for high-value transactions which are based on ‘real time’. The minimum amount to be remitted through RTGS is Rupees Two Lakhs. There is no upper limit.
Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) is an instant electronic funds transfer facility offered by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) which is available 24 x7.
The usage of Prepaid payment instruments (PPIs) for purchase of goods & services and funds transfers has increased considerably in recent years. The value of transactions through PPI Cards (which include mobile prepaid instruments, gift cards, foreign travel cards & corporate cards) & mobile wallets have jumped drastically from Rs.105 billion and Rs. 82 billion respectively in 2014-15 to Rs. 277 billion and Rs. 532 billion respectively in 2016-17.
Challenges
-
Security Risks
External threats such as hacking, sniffing and spoofing expose banks to security risks. Banks are also exposed to internal risks especially frauds by employees / employees in collusion with customers
-
Financial Literacy / Customer Awareness
Lack of knowledge amongst people to use e-banking facilities is the major constraint in India.
-
Fear factor
One of the biggest hurdle in online banking is preference to conventional banking method by older generation and mostly people from the rural areas. The fear of losing money in the online transaction is a barrier to usage of e-banking.
-
Training
Lack of adequate knowledge and skills is a major deterrent for employees to deal with the innovative and changing technologies in banks. Training at all levels on the changing trends in IT is the requirement of the day for the banks.