Management Information System (MIS) Concept, Types, Process, Advantages and Disadvantages
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization.
The study of the management information systems testing people, processes and technology in an organizational context.
Management Information Systems (MIS) refer to the integration of information technology, individuals, and business procedures to capture, store, and process data with the objective of generating valuable insights for day-to-day decision-making. By extracting data from diverse sources, MIS facilitates the production of information that empowers decision-makers and fuels business growth.
- Need for Management Information Systems (MIS)
Management Information Systems (MIS) play a vital role in enabling decision-makers to access essential information for making effective choices. These systems also facilitate seamless communication within and outside the organization. Internally, employees can readily access the necessary information for day-to-day operations, while externally, communication with customers and suppliers is streamlined through features like Short Message Service (SMS) and Email integrated within the MIS system.
Additionally, MIS systems serve as comprehensive record-keeping tools, meticulously capturing all business transactions of an organization. They act as a reliable reference point, providing a historical record and valuable insights into past activities and financial dealings.
Components of Management Information Systems (MIS):
- People: The users who interact with the information system, including employees and managers.
- Data: The recorded information that the system processes and stores, such as transaction data and business records.
- Business Procedures: The set of established procedures and guidelines for data recording, storage, and analysis within the system.
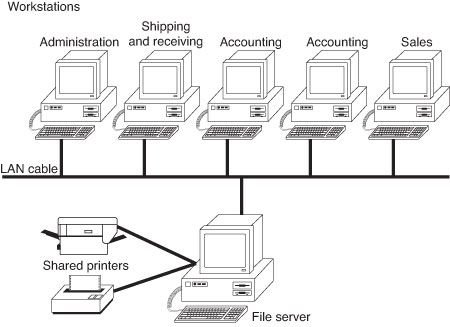
- Hardware: The physical components that make up the system, including servers, workstations, networking equipment, and printers.
- Software: The programs and applications used to manage and handle the data, such as spreadsheet software and database systems.
Types of Information Systems
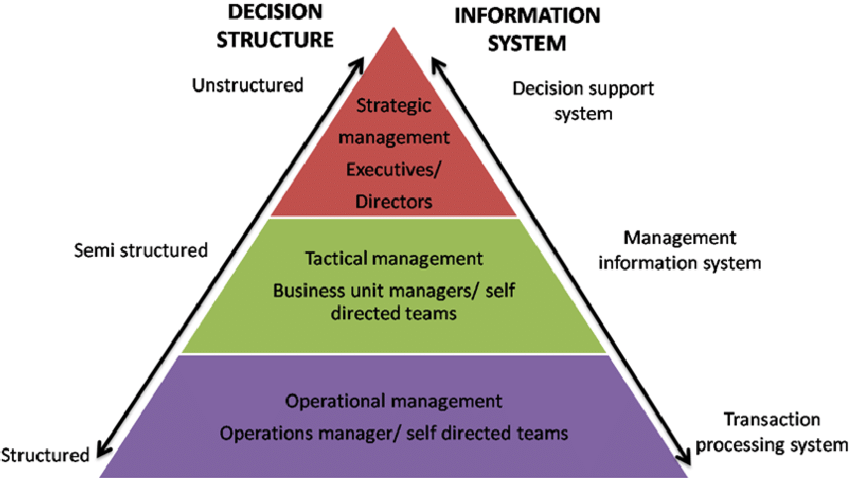
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): Used to record and manage day-to-day business transactions. An example is a Point of Sale (POS) system, which tracks daily sales.
- Management Information Systems (MIS): These systems guide middle-level managers in making semi-structured decisions. They use data from the Transaction Processing System as input.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): Utilized by top-level managers for semi-structured decision-making. DSS systems receive data from the Management Information System and external sources like market forces and competitors.
Process of Management Information System (MIS):
- Data Collection:
- Source of Data: MIS collects data from various sources, including internal databases, external sources, and manual inputs.
- Methods: Data may be collected through automated systems, surveys, or direct inputs.
- Data Processing:
- Transformation: Raw data is processed and transformed into meaningful information.
- Analysis: MIS conducts data analysis to derive insights and trends.
- Normalization: Data is organized and normalized for consistency.
- Information Storage:
- Database: Processed information is stored in databases or data warehouses.
- Structured Storage: MIS organizes data in a structured manner for easy retrieval.
- Information Retrieval:
- Querying: Users can query the MIS for specific information.
- Reporting: MIS generates reports, dashboards, and summaries based on user needs.
- Information Dissemination:
- Distribution: MIS distributes information to relevant users and stakeholders.
- Presentation: Information is presented in a user-friendly format, such as charts or graphs.
- Decision Support:
- Analysis Tools: MIS provides decision support tools for managers.
- Scenario Analysis: Managers can use MIS for scenario analysis and planning.
- Feedback Mechanism:
- Monitoring: MIS monitors the implementation of decisions.
- Feedback Loop: MIS establishes a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
Advantages of Management Information System (MIS):
-
Improved Decision-Making:
- Access to Information: MIS provides timely and accurate information for decision-making.
- Informed Choices: Managers can make well-informed decisions based on real-time data.
-
Enhanced Efficiency:
- Automation: MIS automates routine tasks, reducing manual effort.
- Streamlined Processes: Efficiency is improved through streamlined workflows.
-
Strategic Planning:
- Long-Term Insights: MIS supports strategic planning with historical data and trend analysis.
- Goal Alignment: Strategic goals can be aligned with available resources and capabilities.
-
Better Communication:
- Centralized Information: MIS centralizes information, facilitating communication across departments.
- Collaboration: Improved communication enhances collaboration among team members.
-
Resource Optimization:
- Resource Allocation: MIS assists in optimal resource allocation.
- Cost Reduction: Identifying inefficiencies leads to cost reduction.
-
Competitive Advantage:
- Market Intelligence: MIS provides insights into market trends and competitor activities.
- Adaptability: Organizations can adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
-
Data Accuracy and Integrity:
- Validation: MIS ensures data accuracy through validation processes.
- Integrity: The system maintains data integrity, preventing inconsistencies.
-
Performance Monitoring:
- KPIs and Metrics: MIS monitors key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular performance monitoring facilitates continuous improvement.
Disadvantages of Management Information System (MIS):
-
Implementation Costs:
- Initial Investment: Setting up an MIS involves significant initial costs.
- Maintenance Expenses: Ongoing maintenance and updates add to the costs.
-
Complex Implementation:
- Technical Expertise: Implementation requires skilled IT professionals.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating MIS with existing systems can be complex.
-
Security Concerns:
- Data Vulnerability: MIS poses security risks, with sensitive data being vulnerable.
- Unauthorized Access: The risk of unauthorized access and data breaches exists.
-
Resistance to Change:
- Employee Resistance: Employees may resist adopting new processes.
- Training Needs: Training is required for employees to adapt to the new system.
-
Dependency on Technology:
- Technical Issues: Dependency on technology exposes the system to technical glitches.
- Downtime Impact: System downtime can disrupt operations.
-
Overemphasis on Data:
- Data Overload: Too much data can lead to information overload.
- Relevance Issues: Not all data may be relevant to decision-makers.
-
Lack of Customization:
- Generic Solutions: Some MIS solutions may offer generic features, limiting customization.
- Business Specificity: Tailoring MIS to specific business needs may be challenging.
-
Ethical Concerns:
- Privacy Issues: MIS may raise concerns about employee privacy.
- Ethical Use: Ethical considerations in data collection and utilization.
Management Information System Role in Decision making process
-
Data Collection and Processing:
- Role of MIS:
- Gathers data from various sources, both internal and external.
- Processes raw data into meaningful information through sorting, summarizing, and analyzing.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Decision-makers have access to comprehensive and organized data.
- Raw data is transformed into actionable insights for informed decision-making.
-
Information Accessibility:
- Role of MIS:
- Centralizes information, making it easily accessible to authorized users.
- Utilizes user-friendly interfaces for querying and retrieving information.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Managers can quickly access the information they need.
- Reduces the time and effort required to gather relevant data for decision-making.
-
Decision Support Tools:
- Role of MIS:
- Provides decision support tools such as reports, dashboards, and data visualization.
- Facilitates ad-hoc querying and analysis for specific decision needs.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Decision-makers can visually interpret complex data.
- Supports data-driven decision-making through interactive tools.
-
Strategic Planning Support:
- Role of MIS:
- Offers historical data and trend analysis for strategic planning.
- Aligns organizational goals with available resources through data insights.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Enables strategic decisions based on long-term trends.
- Assists in setting realistic goals and objectives.
- Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Role of MIS:
- Tracks and monitors key performance indicators relevant to organizational objectives.
- Generates performance reports and alerts.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Decision-makers can assess the success of current strategies.
- Allows for adjustments based on real-time performance data.
-
Operational Efficiency:
- Role of MIS:
- Identifies operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Automates routine tasks, reducing manual effort.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Supports decisions aimed at improving operational processes.
- Enhances overall organizational efficiency.
-
Forecasting and Predictive Analysis:
- Role of MIS:
- Utilizes data trends and patterns for forecasting.
- Integrates predictive analytics to anticipate future outcomes.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Helps in making proactive decisions based on anticipated trends.
- Reduces reliance on reactive decision-making.
-
Collaboration and Communication:
- Role of MIS:
- Facilitates communication and collaboration among team members.
- Enables sharing of information and reports.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Improves communication channels for decision-making teams.
- Encourages collaborative decision-making processes.
-
Risk Management:
- Role of MIS:
- Identifies and assesses potential risks through data analysis.
- Offers scenario analysis for risk evaluation.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Assists in making risk-informed decisions.
- Allows for the formulation of risk mitigation strategies.
-
Feedback Mechanism:
- Role of MIS:
- Establishes a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
- Monitors the implementation of decisions.
- Impact on Decision Making:
- Decision-makers receive feedback on the effectiveness of their decisions.
- Supports a dynamic and adaptive decision-making process.