SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. It involves assessing factors within the organization’s control, such as resources, capabilities, and processes, to determine competitive advantages and areas needing improvement. Additionally, SWOT analysis evaluates external factors like market trends, competitor actions, and regulatory changes to uncover potential avenues for growth and challenges to address. By synthesizing this information, organizations can develop strategies to capitalize on strengths, mitigate weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and defend against threats, ultimately enhancing their competitive position and guiding decision-making processes.
Elements of a SWOT analysis:
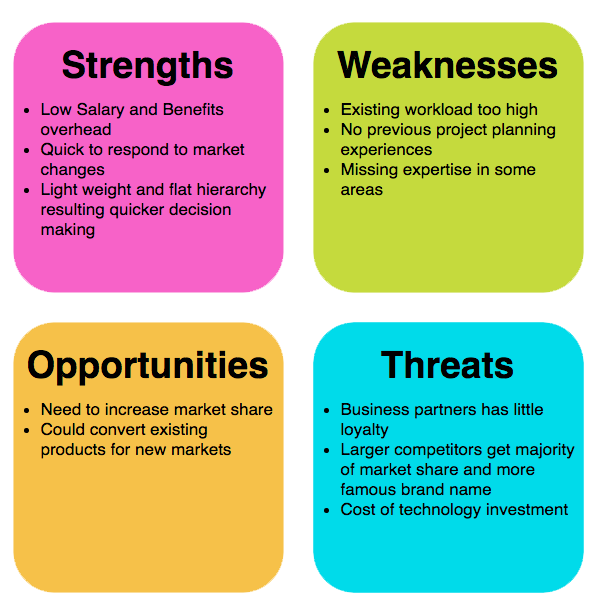
- Strengths:
Internal attributes and resources that give the organization a competitive advantage. These can include factors such as strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, proprietary technology, efficient processes, and financial stability.
- Weaknesses:
Internal factors that place the organization at a disadvantage compared to competitors. Weaknesses may include areas such as limited resources, outdated technology, poor brand perception, inefficient processes, and lack of expertise or talent.
- Opportunities:
External factors or trends in the business environment that the organization could exploit to its advantage. Opportunities may arise from market growth, emerging trends, technological advancements, changes in consumer preferences, or regulatory changes.
- Threats:
External factors that could negatively impact the organization’s performance or pose risks to its success. Threats may come from factors such as intense competition, economic downturns, changing regulatory landscapes, disruptive technologies, or shifts in consumer behavior.
Factors affecting SWOT Analysis:
-
Scope and Objectives:
Clearly defining the scope and objectives of the analysis ensures that relevant factors are considered and that the analysis remains focused on its intended purpose.
-
Data Quality:
The accuracy and reliability of the data used in the analysis directly impact the validity of the findings. Using up-to-date, accurate, and comprehensive data sources is essential.
-
Perspective and Bias:
Different stakeholders may have varying perspectives and biases that influence their perception of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It’s crucial to consider multiple viewpoints to ensure a balanced analysis.
-
Expertise and Knowledge:
The expertise and knowledge of the individuals conducting the analysis can affect the depth and insightfulness of the findings. Involving individuals with diverse backgrounds and expertise can enhance the quality of the analysis.
-
External Environment:
Changes in the external business environment, such as market trends, competitor actions, regulatory changes, economic conditions, and technological advancements, can impact the validity of the analysis. Regularly updating the analysis to reflect changes in the external environment is essential.
-
Internal Dynamics:
Internal factors such as organizational culture, leadership, resource allocation, and decision-making processes can influence the identification of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understanding internal dynamics is crucial for conducting a realistic SWOT analysis.
- Interrelationships:
Recognizing the interrelationships between different elements of the SWOT analysis is important for understanding how they interact and influence each other. For example, addressing a weakness may create opportunities, or exploiting an opportunity may mitigate a threat.
- Time Constraints:
Time constraints can limit the depth and thoroughness of the analysis. It’s essential to allocate sufficient time and resources to conduct a comprehensive SWOT analysis effectively.
Benefits of SWOT Analysis:
-
Strategic Planning:
SWOT analysis provides a structured framework for organizations to assess their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. This information is invaluable for strategic planning, helping organizations align their resources and capabilities with their goals and objectives.
-
Improved Decision Making:
By identifying key factors influencing the organization’s performance and competitive position, SWOT analysis enables informed decision making. It helps organizations prioritize initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and capitalize on opportunities while mitigating potential risks.
-
Enhanced Competitive Positioning:
Understanding the organization’s strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors, as well as market opportunities and threats, enables organizations to develop strategies to enhance their competitive positioning. SWOT analysis helps organizations identify unique selling points, differentiate themselves in the market, and capitalize on competitive advantages.
-
Risk Management:
By identifying potential threats and weaknesses, SWOT analysis helps organizations anticipate risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. It enables proactive risk management, reducing the likelihood of negative impacts on the organization’s performance and reputation.
-
Facilitates Change Management:
SWOT analysis provides valuable insights into the internal and external factors affecting the organization, making it a useful tool for change management initiatives. It helps organizations anticipate resistance to change, identify areas requiring improvement, and develop strategies to overcome barriers to change.
-
Enhanced Communication and Alignment:
SWOT analysis fosters communication and alignment within the organization by providing a common understanding of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It facilitates collaboration among stakeholders, promotes transparency in decision making, and ensures that everyone is working towards common goals and objectives.