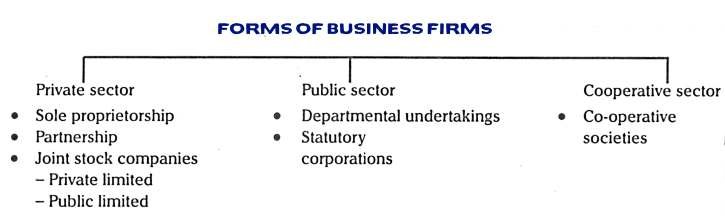
Public Sectors
Public sector refers to government-owned or government-controlled organizations and entities that provide goods and services to the general public. These include government agencies, departments, and enterprises responsible for delivering essential services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and public safety. The public sector operates with the goal of serving the public interest and promoting the welfare of society.
Role of Public Sectors:
-
Service Provision:
Public sectors provide essential services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and utilities to ensure universal access and meet societal needs.
-
Infrastructure Development:
Public sectors invest in and maintain infrastructure such as roads, bridges, airports, and utilities to support economic growth and social development.
-
Regulation and Oversight:
Public sectors regulate industries and enforce laws to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and environmental sustainability.
-
Employment Opportunities:
Public sectors create jobs and offer stable employment opportunities, contributing to economic stability and reducing unemployment rates.
-
Social Welfare:
Public sectors implement welfare programs, social security systems, and poverty alleviation initiatives to support vulnerable populations and promote social equity.
-
Investment in Research and Innovation:
Public sectors fund research and development initiatives, support innovation, and promote technological advancement to drive economic growth and improve quality of life.
-
Strategic Investments:
Public sectors make strategic investments in key sectors such as healthcare, education, and technology to foster long-term economic competitiveness and prosperity.
-
Public Goods Provision:
Public sectors supply public goods such as national defense, law enforcement, and disaster relief that benefit society as a whole and are not provided adequately by the private sector.
Importance of Public Sectors:
-
Service Provision:
Public sectors ensure the delivery of essential services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and utilities to all members of society, regardless of their ability to pay.
-
Social Equity:
Public sectors promote social equity by providing access to basic services and support to disadvantaged and marginalized populations, reducing inequalities and improving social welfare.
-
Economic Stability:
Public sectors play a vital role in stabilizing the economy through strategic investments, employment generation, and regulation of key industries, contributing to economic growth and resilience.
-
Infrastructure Development:
Public sectors invest in and maintain infrastructure that forms the backbone of economic activity, including roads, bridges, airports, and utilities, supporting productivity and connectivity.
-
Regulation and Oversight:
Public sectors regulate industries, enforce laws, and provide oversight to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, environmental sustainability, and public safety.
-
Innovation and Research:
Public sectors fund research and innovation initiatives, support scientific advancements, and promote technological progress, driving economic development and improving quality of life.
-
National Security:
Public sectors are responsible for ensuring national security through defense, law enforcement, and emergency response services, safeguarding the well-being and sovereignty of the nation.
-
Public Goods Provision:
Public sectors supply public goods such as defense, public safety, and environmental protection that benefit society as a whole and are not adequately provided by the private sector.
Private Sectors
Private Sector comprises privately-owned businesses and enterprises that operate for profit and are not under direct government control. It encompasses a wide range of industries and sectors, including manufacturing, retail, finance, technology, and services. Private sector businesses are driven by market forces and aim to maximize profits and shareholder value. They play a significant role in driving economic growth, creating employment opportunities, and fostering innovation and competition within the economy.
Role of Private Sectors:
-
Economic Growth:
Private sectors drive economic growth by investing capital, creating jobs, and fostering innovation, entrepreneurship, and productivity enhancements.
-
Employment Generation:
Private sectors are major sources of employment, offering job opportunities across various industries and sectors, contributing to poverty reduction and economic stability.
-
Innovation and Technology:
Private sectors spur innovation and technological advancement through research and development, leading to the creation of new products, processes, and services that drive progress and competitiveness.
-
Efficiency and Competition:
Private sectors promote efficiency and competition by operating in a market-driven environment, incentivizing businesses to improve quality, reduce costs, and innovate to meet consumer demands.
-
Wealth Creation:
Private sectors generate wealth by generating profits and returns on investments, stimulating economic activity, and contributing to the accumulation of capital for future growth and development.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Private sectors engage in CSR initiatives, including philanthropy, environmental sustainability, and community development projects, demonstrating their commitment to social responsibility and contributing to the well-being of society.
Importance of Private Sectors:
-
Economic Growth:
Private sectors are primary drivers of economic growth through investments, entrepreneurship, and productivity improvements, leading to increased GDP and overall prosperity.
-
Job Creation:
Private sectors generate employment opportunities across various industries and sectors, reducing unemployment rates and providing livelihoods for millions of people worldwide.
-
Innovation and Technology:
Private sectors spur innovation and technological advancement by investing in research and development, leading to the creation of new products, services, and processes that drive progress and competitiveness.
-
Efficiency and Competition:
Private sectors operate in a competitive market environment, driving efficiency, quality improvement, and cost reduction to meet consumer demands and stay competitive.
-
Wealth Creation:
Private sectors generate wealth through profit generation, investment returns, and capital accumulation, fueling economic activity and creating opportunities for wealth creation and distribution.
-
Diversification and Specialization:
Private sectors promote diversification and specialization within the economy, leading to the development of niche markets, specialized skills, and competitive advantages that enhance overall economic resilience and competitiveness.
-
Global Trade and Investment:
Private sectors facilitate global trade and investment by expanding market access, fostering international business relationships, and driving cross-border economic integration, contributing to global economic interconnectedness and prosperity.
-
Inclusive Growth:
Private sectors play a vital role in promoting inclusive growth by providing opportunities for entrepreneurship, skills development, and social mobility, contributing to poverty reduction, social cohesion, and shared prosperity.
Co-operative Sector
Co-operative sector consists of enterprises owned and operated by their members, who pool resources and share ownership to meet common needs and objectives. These organizations operate on democratic principles, with members having equal voting rights regardless of their financial contributions. Cooperatives exist in various sectors, including agriculture, finance, retail, housing, and healthcare, and aim to promote economic participation, social cohesion, and community development through collective action and mutual support.
Role of Co-operative Sector:
-
Community Development:
Cooperatives empower communities by providing collective ownership and democratic control over essential services such as agriculture, finance, housing, and healthcare, leading to local economic development and social cohesion.
-
Economic Participation:
Cooperatives promote economic participation by allowing members to pool resources, share risks, and benefit collectively from their cooperative endeavors, fostering financial inclusion and self-reliance.
-
Job Creation:
Cooperatives generate employment opportunities by creating cooperative enterprises and supporting cooperative businesses, particularly in rural and marginalized areas where traditional employment opportunities may be limited.
-
Access to Services:
Cooperatives provide access to essential services such as banking, credit, insurance, healthcare, education, and utilities to underserved populations, improving their quality of life and enhancing social welfare.
-
Empowerment and Capacity Building:
Cooperatives empower members by promoting democratic decision-making, leadership development, and skills training, enabling individuals to actively participate in their economic and social development.
-
Sustainable Development:
Cooperatives promote sustainable development by adopting environmentally friendly practices, promoting resource conservation, and supporting sustainable agriculture, energy, and production methods.
-
Market Access and Fair Trade:
Cooperatives enable small-scale producers and marginalized groups to access markets, negotiate fair prices, and participate in fair trade practices, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits and reducing market vulnerabilities.
-
Social Responsibility:
Cooperatives embody principles of social responsibility and solidarity by prioritizing the well-being of their members, supporting community development initiatives, and contributing to social and environmental sustainability.
Importance of Co-operative Sector:
-
Community Empowerment:
Cooperatives empower communities by providing collective ownership, democratic control, and equitable distribution of benefits, fostering social cohesion, and promoting inclusive development.
-
Economic Participation:
Cooperatives enable members to actively participate in economic activities, pooling resources, sharing risks, and benefiting collectively from their cooperative endeavors, leading to financial inclusion and self-reliance.
-
Job Creation:
Cooperatives create employment opportunities, particularly in rural and marginalized areas, by establishing cooperative enterprises and supporting cooperative businesses, contributing to poverty reduction and economic stability.
-
Access to Essential Services:
Cooperatives provide access to essential services such as banking, credit, insurance, healthcare, education, and utilities to underserved populations, improving their quality of life and enhancing social welfare.
-
Promotion of Sustainable Development:
Cooperatives promote sustainable development by adopting environmentally friendly practices, supporting sustainable agriculture, energy, and production methods, and prioritizing social and environmental responsibility.
-
Market Access for Small Producers:
Cooperatives enable small-scale producers and marginalized groups to access markets, negotiate fair prices, and participate in fair trade practices, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits and reducing market vulnerabilities.
-
Social Responsibility:
Cooperatives embody principles of social responsibility and solidarity by prioritizing the well-being of their members, supporting community development initiatives, and contributing to social and environmental sustainability.
-
Resilience and Stability:
Cooperatives provide a resilient and stable economic model that is less prone to economic shocks and market fluctuations, fostering long-term sustainability and resilience in communities and economies.