Sources of Consumer Dissatisfaction
01/09/2022 0 By indiafreenotesCustomer satisfaction is an essential aspect of any business. It is vital to keep customers happy and satisfied with your product or service. If you fail to do so, you risk losing them as customers.
Consumer dissatisfaction can arise from various sources, and understanding these sources is crucial for businesses to address issues and improve the overall customer experience. Businesses need to actively monitor and address these sources of consumer dissatisfaction to maintain a positive brand image, foster customer loyalty, and drive long-term success. Regularly seeking customer feedback, analyzing customer interactions, and implementing improvements based on insights are essential steps in minimizing dissatisfaction and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Service-based dissatisfaction
As customers, we are twice as likely to share a negative service experience over a negative product experience. This is because we don’t seek out customer support, but rather it’s foisted upon us.
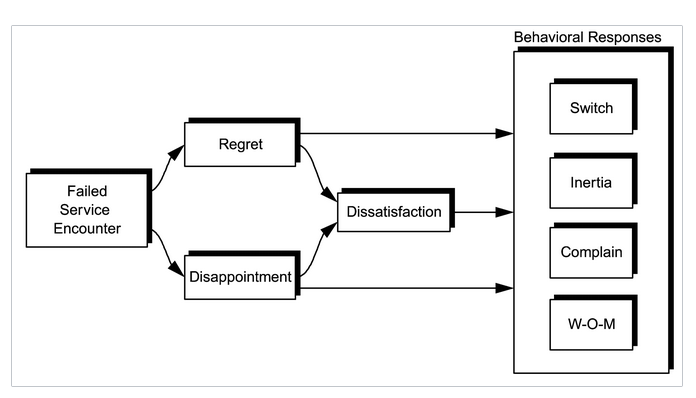
Atomic customer service
While we choose to buy products, we only engage with customer support to complain about a product or service or ask about something that is unclear. If we have to endure long waiting times or repeated escalations to get our issue resolved, these only add salt to injury.
Poor customer service can be defined as the breaking of these principles which have been summarized here:
- Slowness. No one likes to be put on hold, especially for time-sensitive problems. Yet, according to research, the average customer can expect to spend 43 days of their life waiting on hold.
The agony is further prolonged when a customer is ping-ponged from one department to another with no agent taking ownership of the case, because of lack of knowledge or empowerment to make decisions.
- Inaccuracy. It doesn’t matter how fast you answer phones or emails if you’re giving your customers incorrect information about your product or service.
As a minimum, customers expect the information provided to them to be accurate, useful and applicable.
- Inaccessibility. Have you ever had a complaint but no matter how hard you tried, you couldn’t find the company’s phone number or email on their website? Instead, you’re asked to fill in a contact form where more often than not, you don’t receive a response.
Offering limited contact options means more effort for the customer. When we have a problem, we usually want it resolved quickly rather than complete numerous actions to talk to a human.
- Opacity. Transparency in a business context is the open sharing of information from a business to its customers. Who hasn’t waited anxiously in a queue, not knowing how long the wait will be or the reason for the wait?
Product-based dissatisfaction
Most purchasing decisions aren’t entirely rational. You may think you’re buying a new iPhone because of its new camera and features, but subconsciously it’s largely about showing off your status to the world.
Purchases of everyday products are also subject to our emotions. We may like to think that we’re choosing a product based on price, but ultimately our decisions are made because the brand resonates with our real or desired identity.
If a product doesn’t perform as expected, e.g. iPhone’s degenerating battery, we not only question our decision-making methods and the brand we’ve chosen, but also our identity.
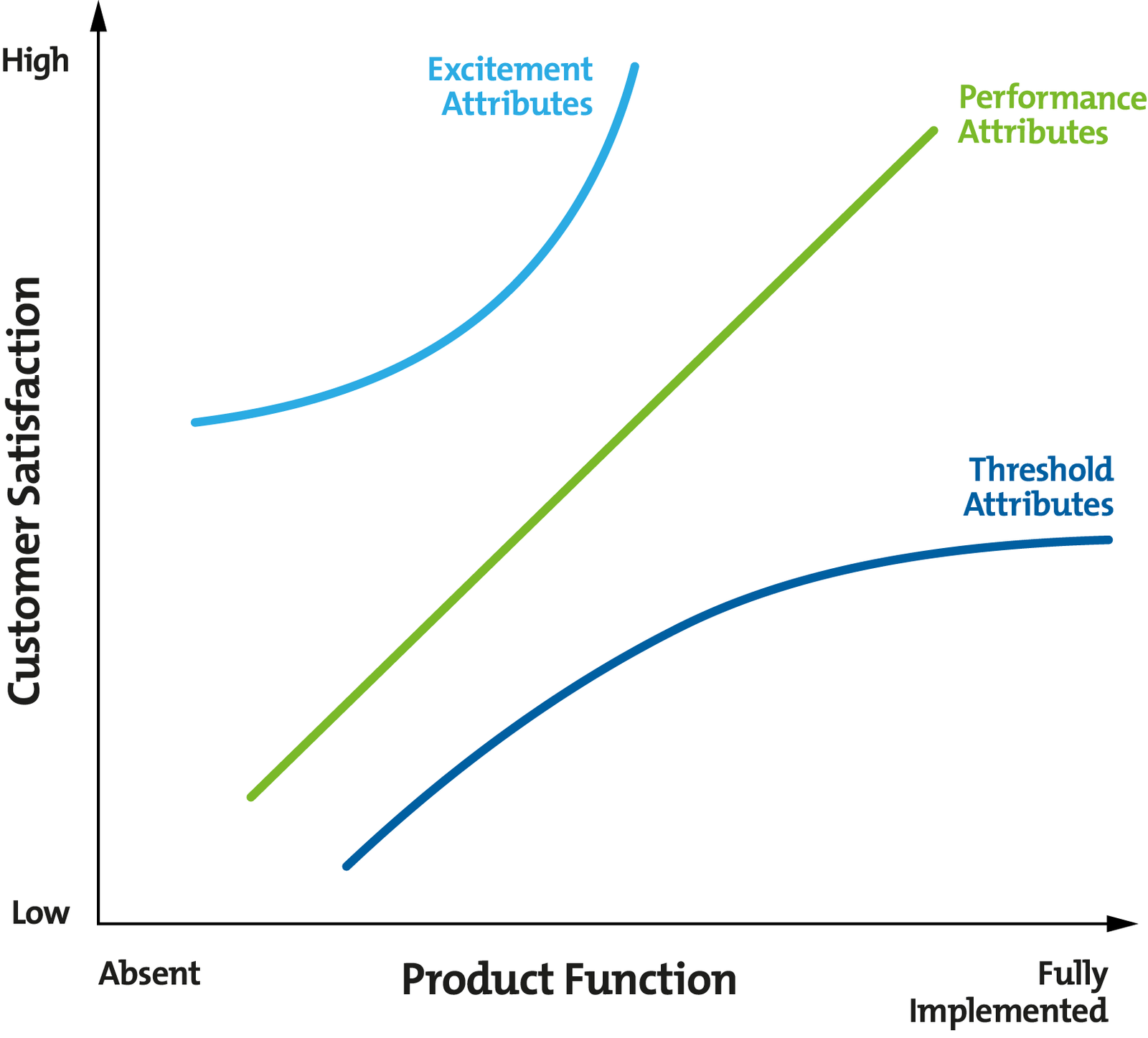
Loyal consumers of a brand may forgive a perceived defect here and there, but this depends on the type of defect. The Kano model assigns three types attributes to products and services:
Threshold attributes (basics). These are the baseline expectations that a product or service should fulfill, e.g. the phone has a battery which lasts a good few hours.
Performance attributes (satisfiers). These increase a customer’s enjoyment of the product, but are not absolutely necessary, e.g. you can take high-quality pictures with your phone.
Excitement attributes (delighters). These features are in no way necessary but delight the customer when they come across them, e.g. the phone can be submerged three feet in water for thirty minutes without lasting damage.
A product which fails to meet threshold expectations will cause even loyal customers to switch brands.
Communication-based dissatisfaction
In an attempt “to project a global message of unity, peace and understanding”, Pepsi released a controversial ad which appeared to trivialize protests against police violence toward minorities. Due to worldwide outrage, the ad was pulled merely one day after its release.
Another example is when language or culture isn’t taken into account when releasing a product to global markets. American Motors made this mistake when naming one of its models, the Matador, which translates to “killer” in Spanish. Although the name intended to convey strength and power, it felt unsurprisingly aggressive and dangerous to Spanish speakers.
Communication failures happen when brands don’t think clearly about how a marketing message or product will come across to their customers, because they chase viral videos rather than focus on the target audience.
Ultimately, the meaning of a message lies with the receiver. If a brand’s messaging fails to address its customers’ needs, wants, beliefs and values, it doesn’t matter how many views the ad gets.
Values-based dissatisfaction
According to a survey by Sprout Social, most customers want brands to take a stand on social and ethical issues. Shared values create trust because we are drawn to people who are similar to ourselves.
In a world of choice, it’s not enough for brands to lead with features and benefits. They also need to communicate clear values.
What happens when a brand violates these values? When Nestlé aggressively marketed baby milk in under-developed countries which inadvertently led to the deaths of infants, it was the target of worldwide boycotts.
Whether customers stand for behaviour that goes against their ethics depends on what the brand stands for. Amazon, for instance, is notorious for treating employees badly. But this does not seem to be affecting customer loyalty all that much because the core of Amazon’s business isn’t built on social values. On the other hand, if the Body Shop would behave in a similar way, their customers would likely be less forgiving.
What’s more, honesty in a relationship increases trust. Dishonesty, on the other hand, leaves the other party wondering what else you’ve lied about.
In the digital age, consumers can look up product/service reviews and discover a company’s history. Yet, the Internet is awash with stories of companies who lied to their customers for personal gain.
Customer satisfaction is a moving target. What makes the customer happy today may not make them happy tomorrow. As discussed in the introduction, it doesn’t drive loyalty behaviour. But the causes of customer dissatisfaction are timeless. They’re a much more solid foundation to build your customer interactions on.
Things to do when you have a dissatisfied customer
If you are dealing with an unhappy customer, here are some things you should do to improve the customer experience.
- Discover what the customer is unhappy about and why? Listen carefully to the complaint. This helps you understand the problem better. Their wants and needs first must be uncovered and defined to see if the features and benefits of your company’s product or services can satisfy those wants and needs.
- Ask questions to clarify the situation. Ask whether we perform to the customer expectations or not?
- Analysis, find the root cause and then improve it.
How to avoid customer dissatisfaction
- Be pro-active. Don’t wait until the customer complains. Surveys and meetings are a great way to understand the customer’s needs.
- Be responsive. When there’s an issue, resolve it immediately. By waiting to resolve an issue can turn minor problems into bigger ones.
- Be honest. Telling customers the truth usually goes over better than lying to them. It will eventually help gain the customer’s respect.
- Be realistic. Not every sale is worth the cost involved in obtaining it. Some customers have expectations that aren’t attainable. In that case, it may be necessary to try to reset the customer’s expectations, or, if that isn’t possible, to suggest that they may be happier by taking their business elsewhere.
Types
Product or Service Quality Issues:
- Defective Products:
Consumers are dissatisfied when they receive products that are defective or do not meet quality standards.
- Poor Service Quality:
In the case of services, dissatisfaction may stem from poor service delivery, errors, or subpar performance.
Customer Service Problems:
- Unresponsive Support:
Lack of responsiveness or slow resolution to customer inquiries or complaints can lead to dissatisfaction.
- Unhelpful Staff:
If customer service representatives are unhelpful, rude, or lack the necessary knowledge, it negatively impacts the customer experience.
Misleading Advertising and Marketing:
- False Claims:
When marketing messages make promises that the product or service cannot fulfill, consumers feel deceived and dissatisfied.
- Misrepresentation:
Misleading product descriptions, images, or pricing can lead to dissatisfaction when the actual experience does not match expectations.
Delivery and Logistics Issues:
- Delayed Deliveries:
Late deliveries, whether for products or services, can result in dissatisfaction, especially if the delay impacts the customer’s plans or expectations.
- Poor Packaging:
Inadequate packaging leading to damaged products upon delivery can contribute to dissatisfaction.
Billing and Pricing Problems:
- Hidden Fees:
Unexpected fees that were not clearly communicated during the purchase process can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction.
- Incorrect Billing:
Billing errors or discrepancies in pricing can erode trust and result in dissatisfaction.
Communication Breakdowns:
- Lack of Communication:
Inadequate communication about order status, changes in policies, or important updates can leave customers feeling uninformed and dissatisfied.
- Poor Transparency:
Lack of transparency in business practices, such as undisclosed terms and conditions, can contribute to dissatisfaction.
Unmet Expectations:
- Failure to Meet Expectations:
When a product or service falls short of what was promised or expected, consumers experience disappointment and dissatisfaction.
- Overpromising and Underdelivering:
Businesses that consistently overpromise and underdeliver may create a pattern of dissatisfaction among customers.
Difficulty in Returns and Refunds:
- Complicated Return Processes:
Cumbersome or unclear return processes can frustrate customers, particularly when trying to return or exchange a product.
- Delayed Refunds:
Delays in processing refunds after returns can lead to dissatisfaction, especially when customers are waiting for their money.
Lack of Personalization:
- Generic Interactions:
Customers may feel dissatisfied if interactions with the business lack personalization and fail to recognize their individual preferences or history.
- Irrelevant Recommendations:
Offering irrelevant products or services based on customer data can lead to dissatisfaction.
Security and Privacy Concerns:
- Data Breaches:
Security breaches that compromise customer information can erode trust and lead to dissatisfaction.
Inadequate Privacy Protection:
Consumers may be dissatisfied if they feel their privacy is not adequately protected, especially in the digital age.
Inconsistent Experiences:
- Inconsistency Across Channels:
Discrepancies in the customer experience across different channels (online, offline, mobile) can result in dissatisfaction.
- Varying Service Quality:
If service quality varies widely across different locations or time periods, customers may experience dissatisfaction.
Unresolved Issues:
- Lack of Resolution:
When customer issues or complaints are not effectively addressed or resolved, dissatisfaction can linger and escalate.
- Poor Handling of Complaints:
Insufficient efforts to address and resolve customer complaints can contribute to ongoing dissatisfaction.
Limited Accessibility:
- Inaccessible Customer Support:
Difficulty reaching customer support, whether due to long wait times, limited channels, or complex automated systems, can lead to dissatisfaction.
- Limited Availability:
Businesses with restricted operating hours or limited availability may frustrate customers seeking assistance.
Cultural Insensitivity:
- Insensitive Marketing:
Marketing messages or campaigns that lack cultural sensitivity can offend certain demographics and result in dissatisfaction.
- Discriminatory Practices:
Any form of discrimination in business practices can lead to dissatisfaction and damage the brand’s reputation.
Competitor Offerings:
- Comparison with Competitors:
If customers find that competitor offerings are more attractive, affordable, or of higher quality, it can lead to dissatisfaction with the current business.
- Lack of Innovation:
Failure to keep up with industry trends or offer innovative solutions may result in customer dissatisfaction.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- More