Governance, risk management and compliance (GRC) is the term covering an organization’s approach across these three practices: governance, risk management, and compliance. The first scholarly research on GRC was published in 2007 where GRC was formally defined as “the integrated collection of capabilities that enable an organization to reliably achieve objectives, address uncertainty and act with integrity.” The research referred to common “keep the company on track” activities conducted in departments such as internal audit, compliance, risk, legal, finance, IT, HR as well as the lines of business, executive suite and the board itself.
GRC
Governance describes the overall management approach through which senior executives direct and control the entire organization, using a combination of management information and hierarchical management control structures. Governance activities ensure that critical management information reaching the executive team is sufficiently complete, accurate and timely to enable appropriate management decision making, and provide the control mechanisms to ensure that strategies, directions and instructions from management are carried out systematically and effectively.
Obligational awareness refers to the ability of the organisation to make itself aware of all of its mandatory and voluntary obligations, namely relevant laws, regulatory requirements, industry codes and organizational standards, as well as standards of good governance, generally accepted best practices, ethics and community expectations. These obligations may be financial, strategic or operational where operational includes such diverse areas as property safety, product safety, food safety, workplace health and safety, asset maintenance, etc.
Risk management is the set of processes through which management identifies, analyzes, and, where necessary, responds appropriately to risks that might adversely affect realization of the organization’s business objectives. The response to risks typically depends on their perceived gravity, and involves controlling, avoiding, accepting or transferring them to a third party, whereas organizations routinely manage a wide range of risks (e.g. technological risks, commercial/financial risks, information security risks etc.).
Compliance means conforming with stated requirements. At an organizational level, it is achieved through management processes which identify the applicable requirements (defined for example in laws, regulations, contracts, strategies and policies), assess the state of compliance, assess the risks and potential costs of non-compliance against the projected expenses to achieve compliance, and hence prioritize, fund and initiate any corrective actions deemed necessary. Compliance administration refers to the administrative exercise of keeping all the compliance documents up to date, maintaining the currency of the risk controls and producing the compliance reports.
Benefits of GRC
- More optimal IT investments
- Improved decision-making
- Elimination of silos
- Reduced fragmentation among divisions and departments
The Capability Model is made up of four components:
LEARN about the organization context, culture and key stakeholders to inform objectives, strategy and actions.
ALIGN strategy with objectives, and actions with strategy, by using effective decision-making that addresses values, opportunities, threats and requirements.
PERFORM actions that promote and reward things that are desirable, prevent and remediate things that are undesirable, and detect when something happens as soon as possible.
REVIEW the design and operating effectiveness of the strategy and actions, as well as the ongoing appropriateness of objectives to improve the organization.
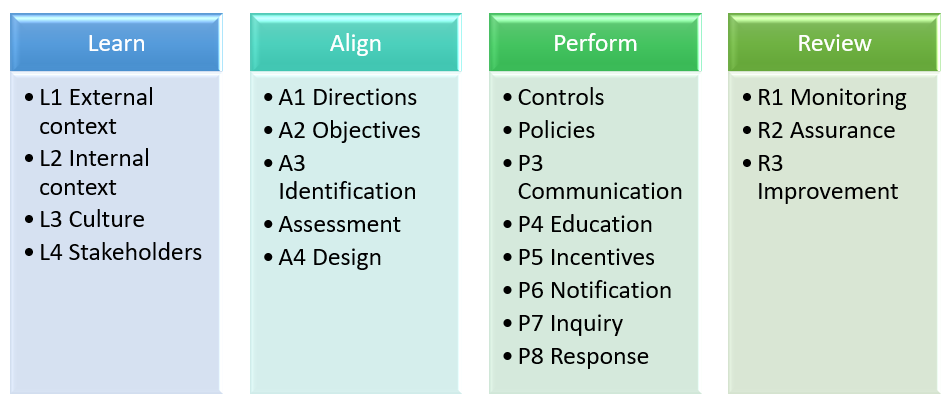
These components outline an iterative continuous improvement process to achieve principled performance and are further decomposed into elements which are then supported by practices, actions and controls. The actions and controls are classified in three types, which organizations can select a mix dependent on their context:
- Proactive
- Detective
- Responsive