Types of Innovation
05/06/2020It is remarkable how many people are under the false assumption that companies are either innovative or not. This is a very polarizing and simplistic perspective that does not take into account the different types of innovations that companies can and do pursue.
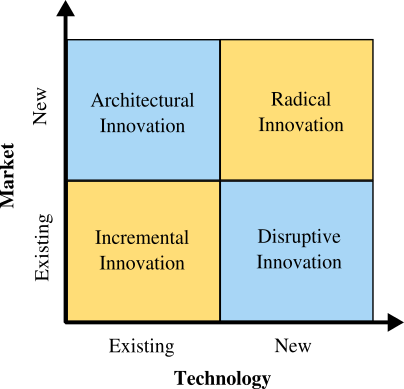
For this post, let’s break down innovation into two dimensions: Technology and Market, which gives us the following 4 types of innovation:
-
Incremental Innovation
Incremental Innovation is the most common form of innovation. It utilizes your existing technology and increases value to the customer (features, design changes, etc.) within your existing market. Almost all companies engage in incremental innovation in one form or another.
Examples include adding new features to existing products or services or even removing features (value through simplification). Even small updates to user experience can add value, for example below is an older version of Constant Contact’s email schedule page.
-
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation, also known as stealth innovation, involves applying new technology or processes to your company’s current market. It is stealthy in nature since newer tech will often be inferior to existing market technology. This newer technology is often more expensive, has fewer features, is harder to use, and is not as aesthetically pleasing. It is only after a few iterations that the newer tech surpasses the old and disrupts all existing companies. By then, it might be too late for the established companies to quickly compete with the newer technology.
There are quite a few examples of disruptive innovation, one of the more prominent being Apple’s iPhone disruption of the mobile phone market. Prior to the iPhone, most popular phones relied on buttons, keypads or scroll wheels for user input. The iPhone was the result of a technological movement that was years in making, mostly iterated by Palm Treo phones and personal digital assistants (PDAs). Frequently you will find that it is not the first mover who ends up disrupting the existing market. In order to disrupt the mobile phone market, Apple had to cobble together an amazing touch screen that had a simple to use interface, and provide users access to a large assortment of built-in and third-party mobile applications.
-
Architectural Innovation
Architectural innovation is simply taking the lessons, skills and overall technology and applying them within a different market. This innovation is amazing at increasing new customers as long as the new market is receptive. Most of the time, the risk involved in architectural innovation is low due to the reliance and reintroduction of proven technology. Though most of the time it requires tweaking to match the requirements of the new market.
In 1966, NASA’s Ames Research Center attempted to improve the safety of aircraft cushions. They succeeded by creating a new type of foam, which reacts to the pressure applied to it, yet magically forms back to its original shape. Originally it was commercially marketed as medical equipment table pads and sports equipment, before having larger success as use in mattresses. This “slow spring back foam” technology falls under architectural innovation. It is commonly known as memory foam.
-
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation is what we think of mostly when considering innovation. It gives birth to new industries (or swallows existing ones) and involves creating revolutionary technology. The airplane, for example, was not the first mode of transportation, but it is revolutionary as it allowed commercialized air travel to develop and prosper.
The four different types of innovation mentioned here – Incremental, Disruptive, Architectural and Radical – help illustrate the various ways that companies can innovate. There are more ways to innovate than these four. The important thing is to find the type(s) that suit your company and turn those into success.
Innovation Strategies
- Proactive
Companies with proactive innovation strategies tend to have strong research orientation and first-mover advantage, and be a technology market leader. They access knowledge from a broad range of sources and take big bets/high risks. Examples include: Dupont, Apple and Singapore Airlines.
The types of technological innovation used in a proactive innovation strategy are:
- Radical: Breakthroughs that change the nature of products and services
- Incremental: The constant technological or process changes that lead to improved performance of products and services.
- Active
Active innovation strategies involve defending existing technologies and markets while being prepared to respond quickly once markets and technologies are proven. Companies using this approach also have broad sources of knowledge and medium-to-low risk exposure; they tend to hedge their bets. Examples include Microsoft, Dell and British Airways.
These companies use mainly incremental innovation with in-house applied research and development.
- Reactive
The reactive innovation strategy is used by companies:
- Which are followers
- Have a focus on operations
- Take a wait-and-see approach
- Look for low-risk opportunities.
They copy proven innovation and use entirely incremental innovators. An example is Ryanair, a budget airline which has successfully copied the no-frills service model of Southwest Airlines.
- Passive
Companies with passive innovation strategies wait until their customers demand a change in their products or services. Examples include automotive supply companies as they wait for their customers to demand changes to specification before implementing these.